
News list
-

Generalist AI for 3D CT
Researchers from the Menze Lab introduce CT-RATE, the first large-scale open dataset pairing 3D chest CT scans with radiology reports. Building on this resource, they develop CT-CLIP and CT-CHAT, foundation models that advance multimodal AI for 3D medical imaging.
-
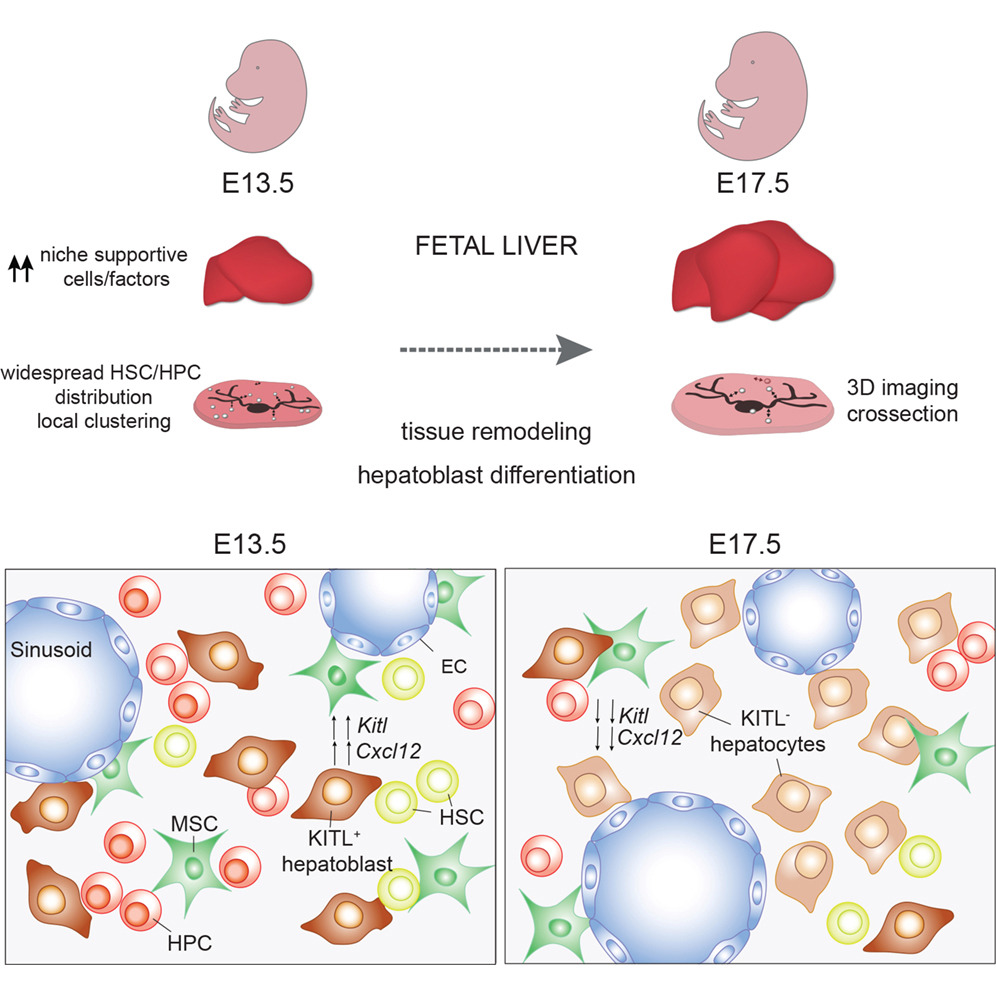
Hepatoblasts Shape Fetal Blood Formation
Researchers reveal how hepatoblasts orchestrate hematopoietic stem cell expansion in the fetal liver. Tissue-scale mapping identifies KIT ligand as a key driver of stem cell maintenance and erythropoiesis.
-

Mapping Cas9 PAM Diversity at Scale
Researchers from the Krauthammer Lab co-developed CRISPR-PAMdb and CICERO, combining metagenomic mining and machine learning to map and predict PAM specificities across thousands of Cas9 enzymes. The study expands the genome editing target space and provides a publicly accessible resource for Cas9 selection and engineering.
-

Targeting DPRs Rescues ALS and FTD Phenotypes
Researchers from the Polymenidou Lab demonstrate that blocking RAN translation - without altering repeat RNAs - rescues behavioral and cellular phenotypes in C9ORF72-related ALS and FTD models. The study identifies dipeptide repeat proteins as primary drivers of disease pathology.
-

DQBM Contributes to NCCR Children and Cancer
The new NCCR Children and Cancer strengthens pediatric oncology research across Switzerland. DQBM researchers contribute expertise in biomedical data analysis and AI for clinical decision making.
-
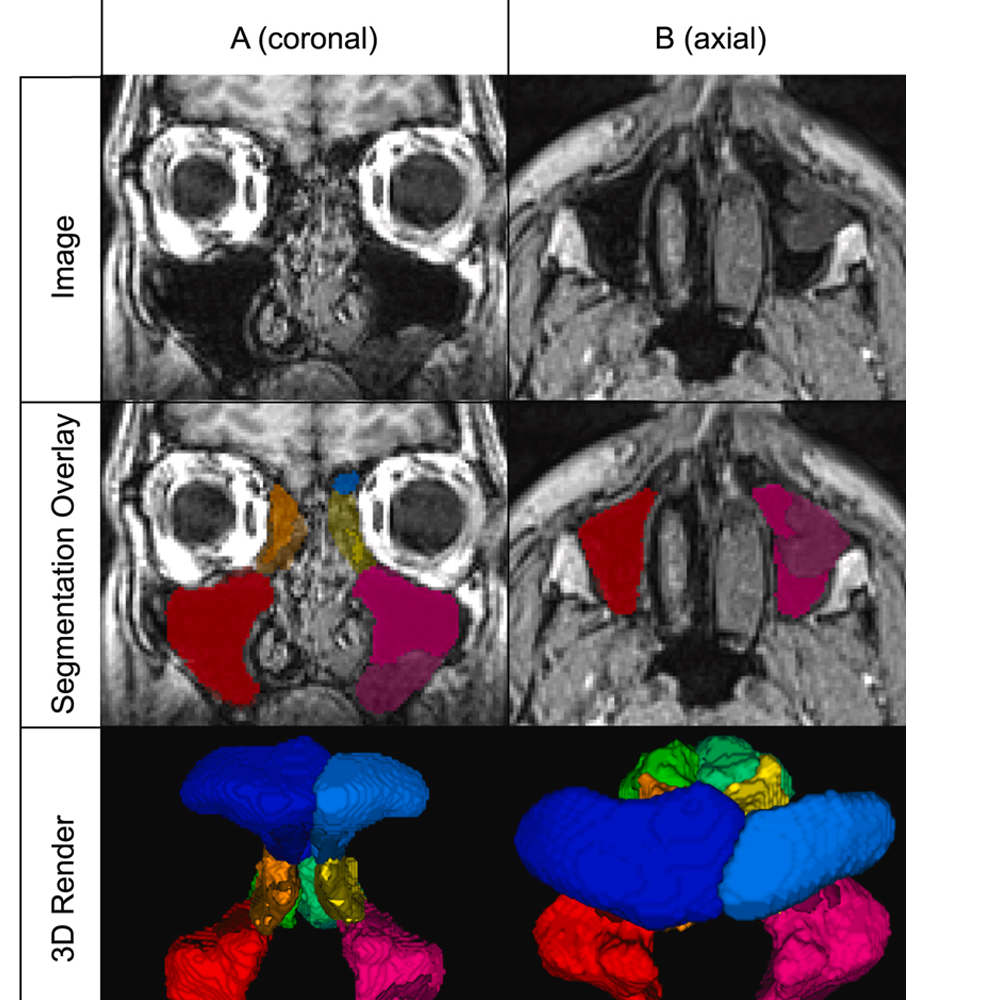
PARASIDE Enables Automated MRI Sinus Analysis
Researchers from the Menze Lab contributed to PARASIDE, the first fully automated T1-weighted MRI tool for whole paranasal sinus segmentation and disease scoring. The system enables objective, radiation-free assessment of chronic rhinosinusitis severity.
-
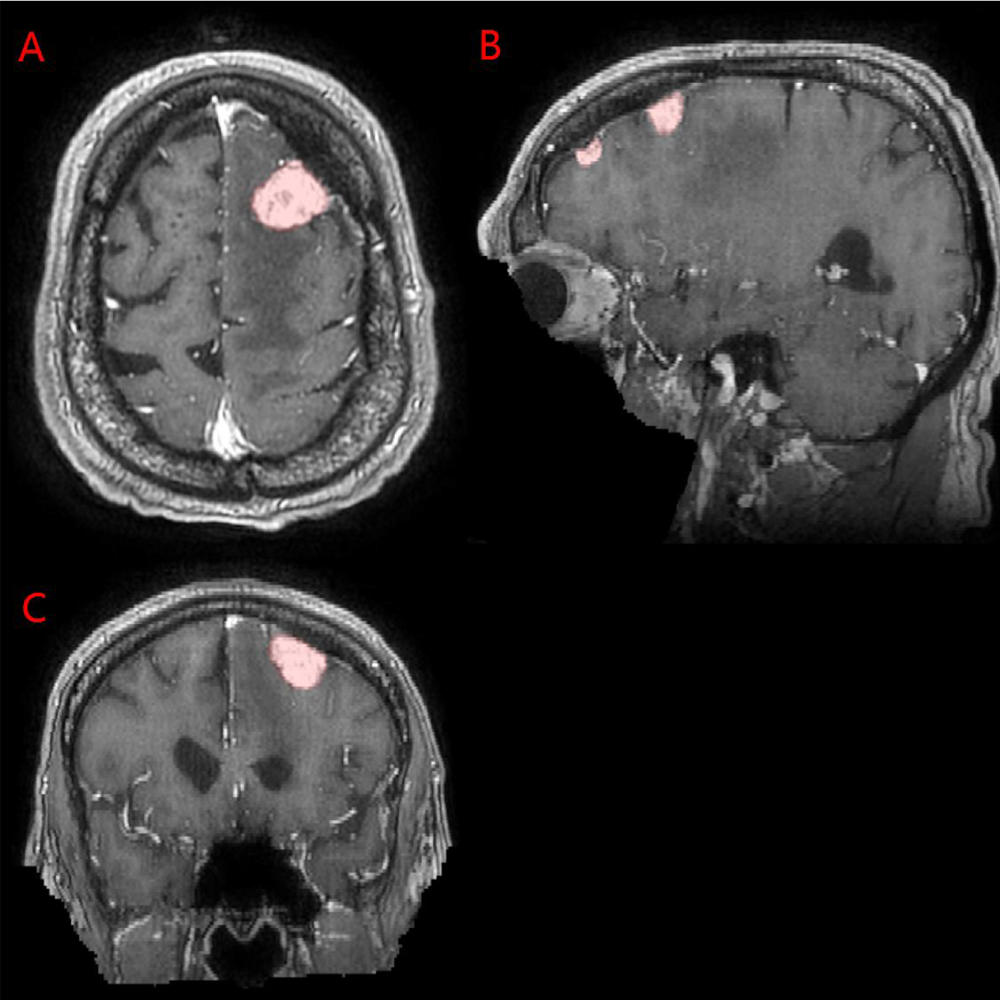
New BraTS-MEN-RT Dataset Published
Researchers from the Menze Lab contributed to the largest multi-institutional dataset of radiotherapy planning MRIs for meningioma segmentation. The open-access resource supports the development of clinically robust AI tools for radiotherapy workflows.
-
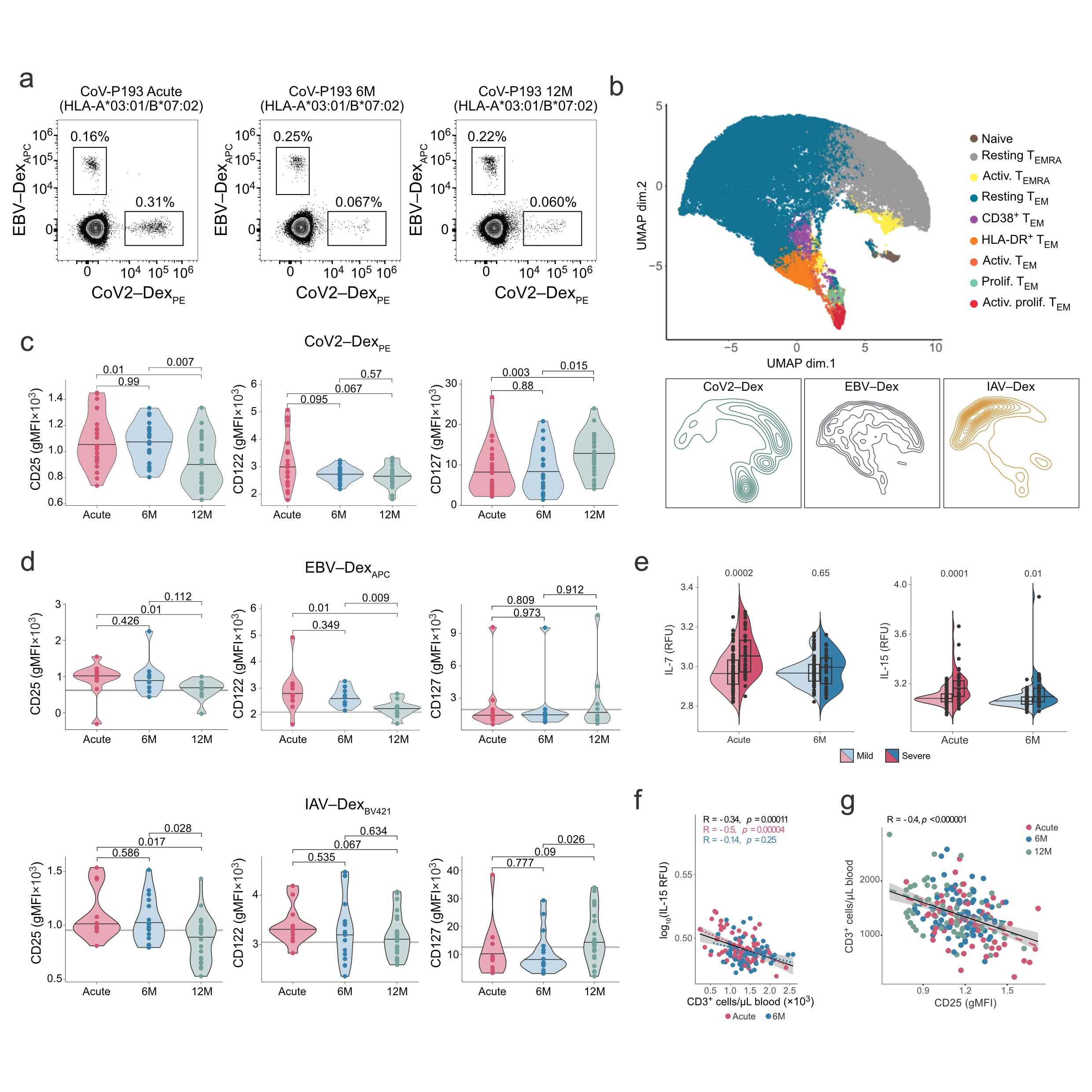
Persistent T Cell Dysregulation After SARS-CoV-2 Infection
A study from the Boyman Lab shows that homeostatic cytokine receptor dysregulation persists for up to one year after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. The findings reveal prolonged T cell activation beyond virus-specific responses, highlighting sustained immune imbalance even after clinical recovery.
-

Robust Fetal Brain MRI Segmentation Across Pathologies
A new NeuroImage study presents a data-driven strategy that improves automated fetal brain MRI segmentation, particularly in severe pathological cases.
-

Antibiotic Resistance Patterns Mapped in Ghana
Nicole Joller and co author Anna Estrada Brull trace how regulatory T cells moved from controversial concept to Nobel Prize winning discovery and outline how this knowledge drives new therapies for autoimmunity and cancer.
-

Microbial Siderophores Expand Plant Iron Uptake
A new Nature Plants Perspective co-authored by DQBM proposes a revised framework for plant iron nutrition that integrates microbial siderophores as a central component.
-
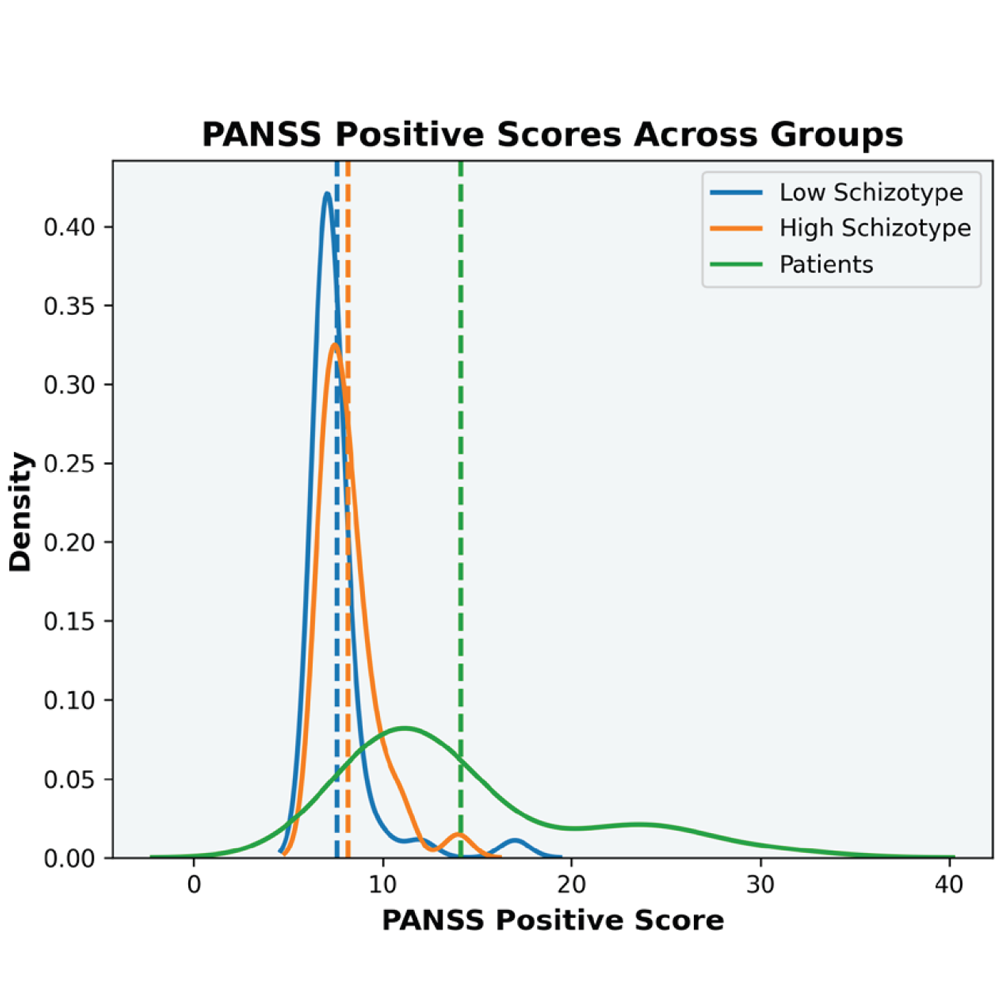
Uncertainty-Aware Speech Analysis in Psychosis
Researchers at DQBM present a multimodal model that improves speech-based assessment across the psychosis spectrum by explicitly modeling uncertainty.
-
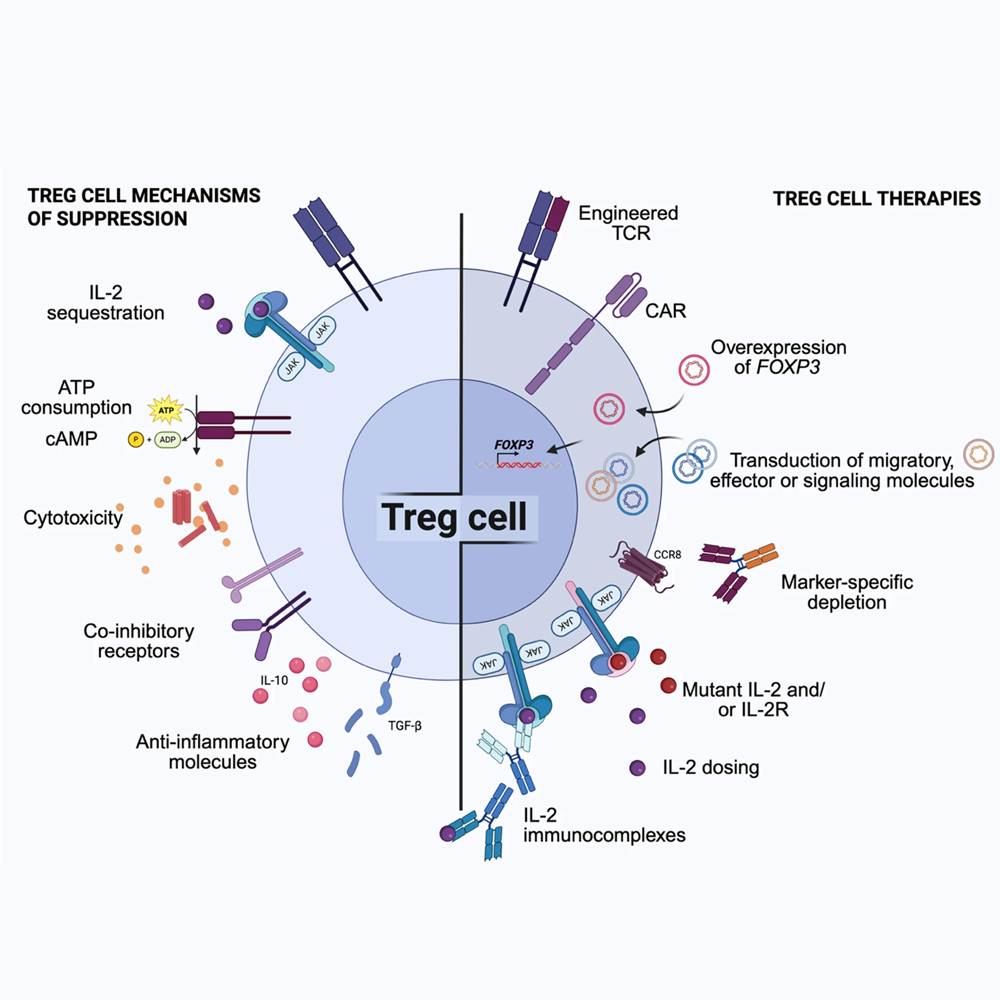
Review celebrates Nobel Treg cell breakthroughs
Nicole Joller and co author Anna Estrada Brull trace how regulatory T cells moved from controversial concept to Nobel Prize winning discovery and outline how this knowledge drives new therapies for autoimmunity and cancer.
-
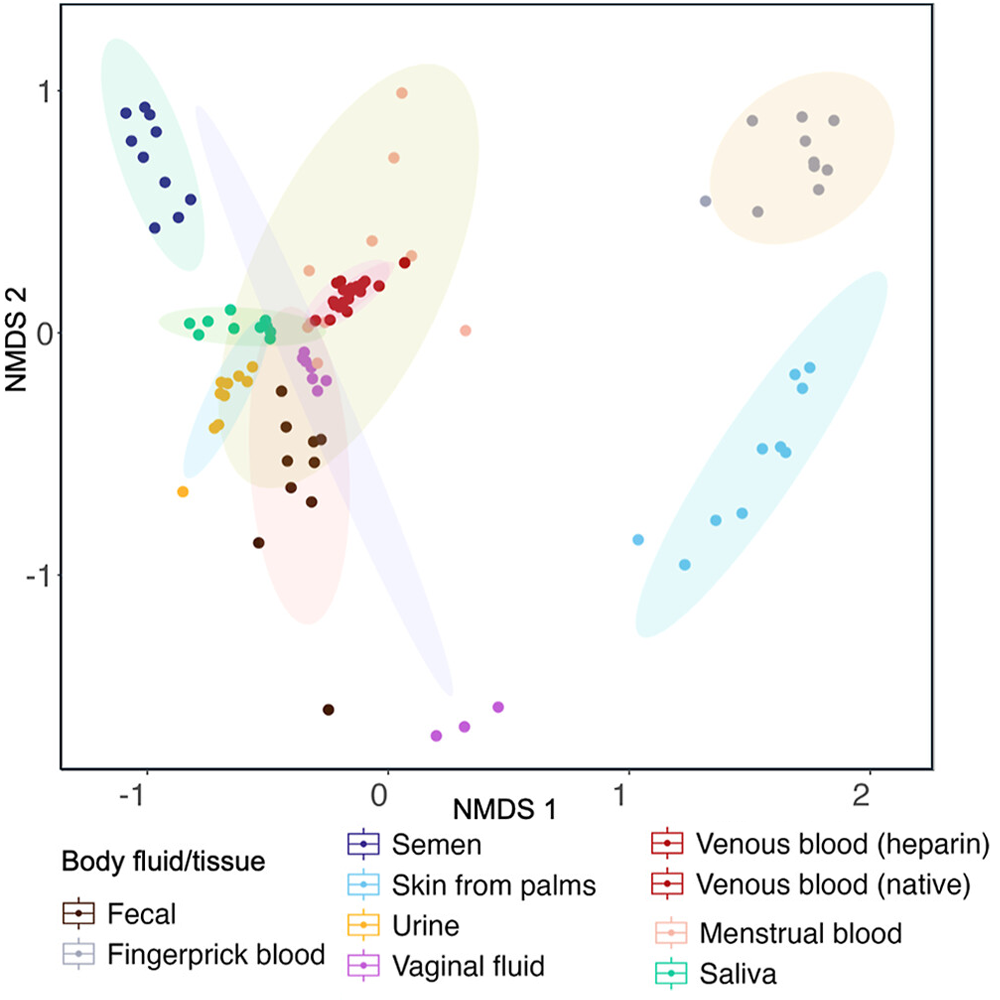
Metabolomics sharpens forensic body fluid ID
A new pilot study co authored by the Kümmerli Lab shows that untargeted metabolomics can distinguish nine different body fluids and tissues using LC QTOF MS. The work identifies candidate metabolite markers that could form the basis of future confirmatory forensic tests.
-

DQBM celebrates Christmas at Ziegelhütte
The DQBM community wrapped up the year with an outdoor Christmas party at Ziegelhütte, starting with fondue and Glühwein and ending with music and a friendly Kegeln competition.
-
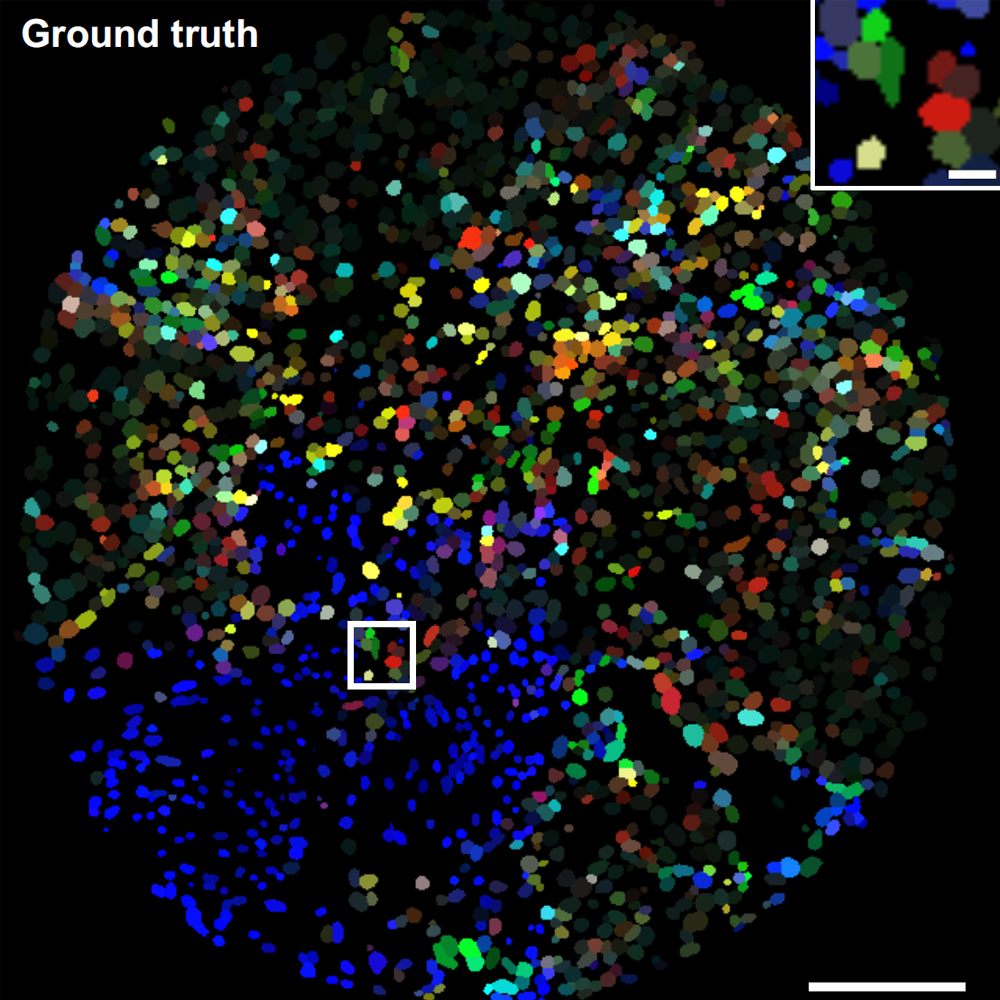
CISI Method Doubles IMC Multiplexing Power
DQBM researchers, together with partners at University Hospital Zurich, ZHAW and ETH Zurich, report a participatory study co-designing OncoSupport+, a patient centered app for supportive cancer care. The work highlights digital screening, personalized information, and usability factors for adoption.
-
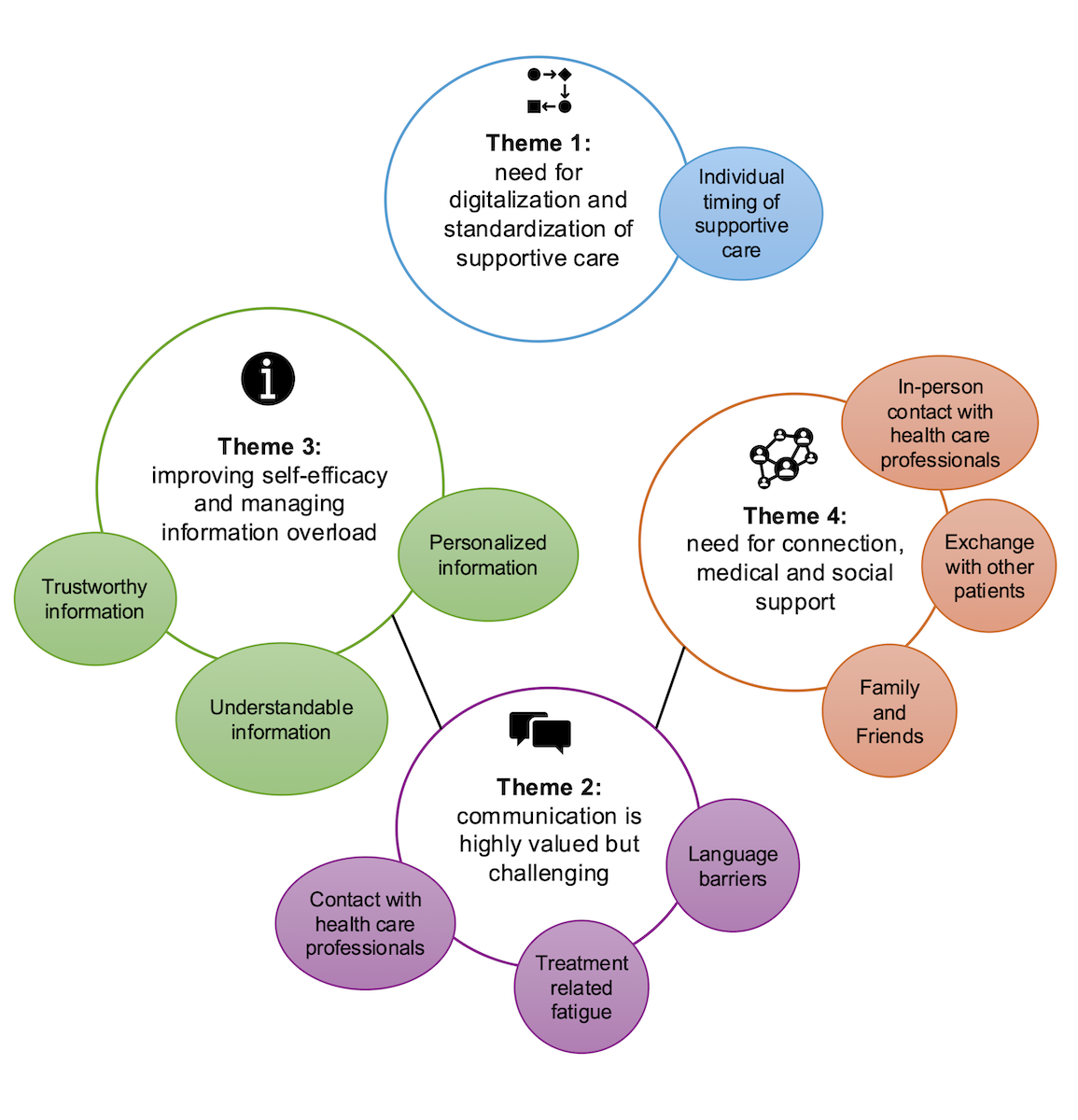
Krauthammer Lab co-designs OncoSupport+ for supportive cancer care
DQBM researchers, together with partners at University Hospital Zurich, ZHAW and ETH Zurich, report a participatory study co-designing OncoSupport+, a patient centered app for supportive cancer care. The work highlights digital screening, personalized information, and usability factors for adoption.
-
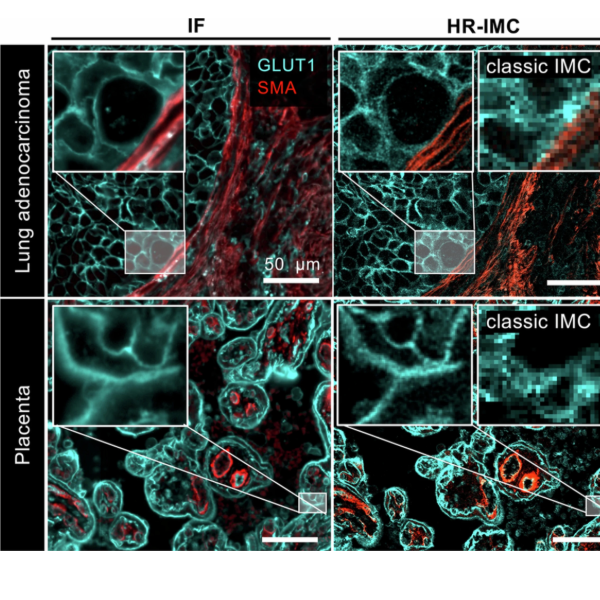
High resolution IMC maps subcellular structures
A Nature Methods study led by DQBM’s Bodenmiller Lab introduces high resolution imaging mass cytometry that resolves submicrometer features and improves cell segmentation, extending IMC into the subcellular regime.
-
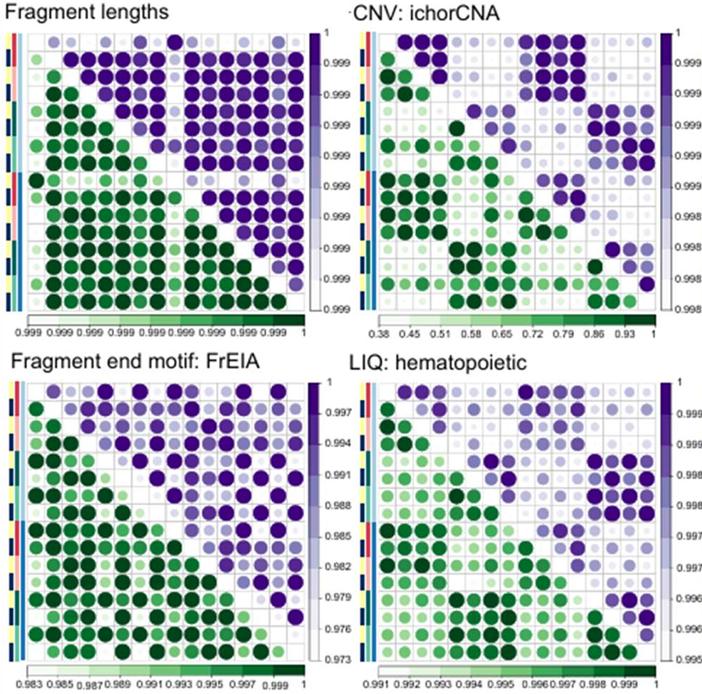
Benchmarking preprocessing for cfDNA fragmentomics
DQBM’s Krauthammer Lab and collaborators benchmark how bioinformatics preprocessing affects cell free DNA fragment analysis, finding most features robust and offering practical recommendations for cancer detection studies.
-

TDP 43 PET tracers show selective, high affinity binding
Nature Communications reports two fluorine 18 PET ligands that bind aggregated TDP 43 with high affinity and selectivity over Aβ, Tau, and α synuclein. ACI 19626 is prioritized for first in human evaluation.
-

DQBM PhD Candidate Ibrahim Hamamci Awarded 2025 Google PhD Fellowship
We congratulate our PhD candidate Ibrahim Ethem Hamamci from the Department of Quantitative Biomedicine (DQBM) at the University of Zurich on receiving the prestigious 2025 Google PhD Fellowship. This award recognises his exceptional and innovative work in machine learning for medical imaging.
-
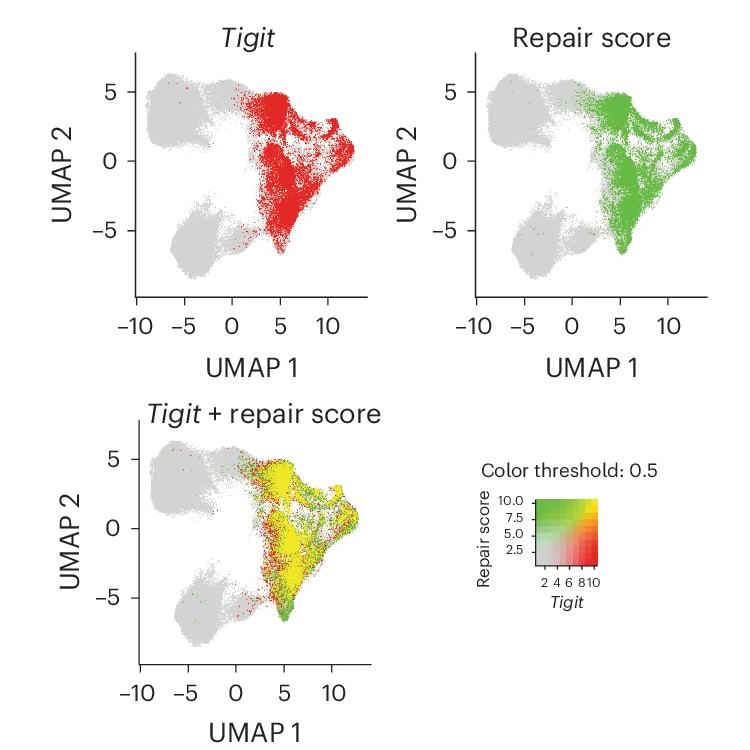
TIGIT promotes tissue repair in T cells
The Joller Lab reveals a novel role for the co-inhibitory receptor TIGIT in driving tissue-protective functions in Treg cells following viral infection.
-

DQBM Engaged in Swiss-Japanese Dialogue on AI and Society
Michael Krauthammer, head of the DQBM, participated in a UZH-led exchange with Japanese partners, addressing the societal impact of AI in fields such as medicine and law. The initiative aims to strengthen international academic collaboration.
-
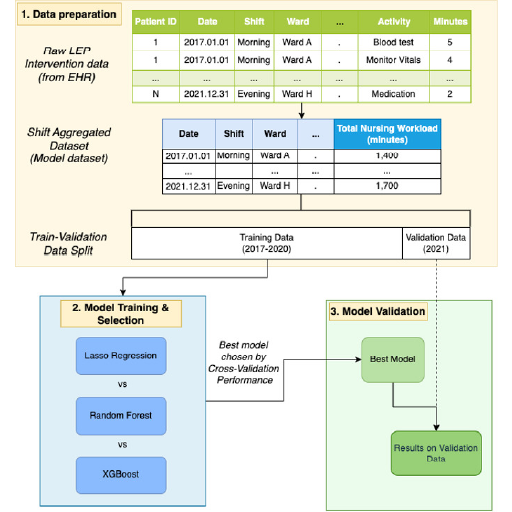
Machine Learning Improves Nurse Workload Prediction
Researchers from the Krauthammer Lab developed a machine learning model that predicts nursing workload with 25% greater accuracy than traditional methods. The study, conducted with the University Hospital Zurich, was published in JMIR.
-
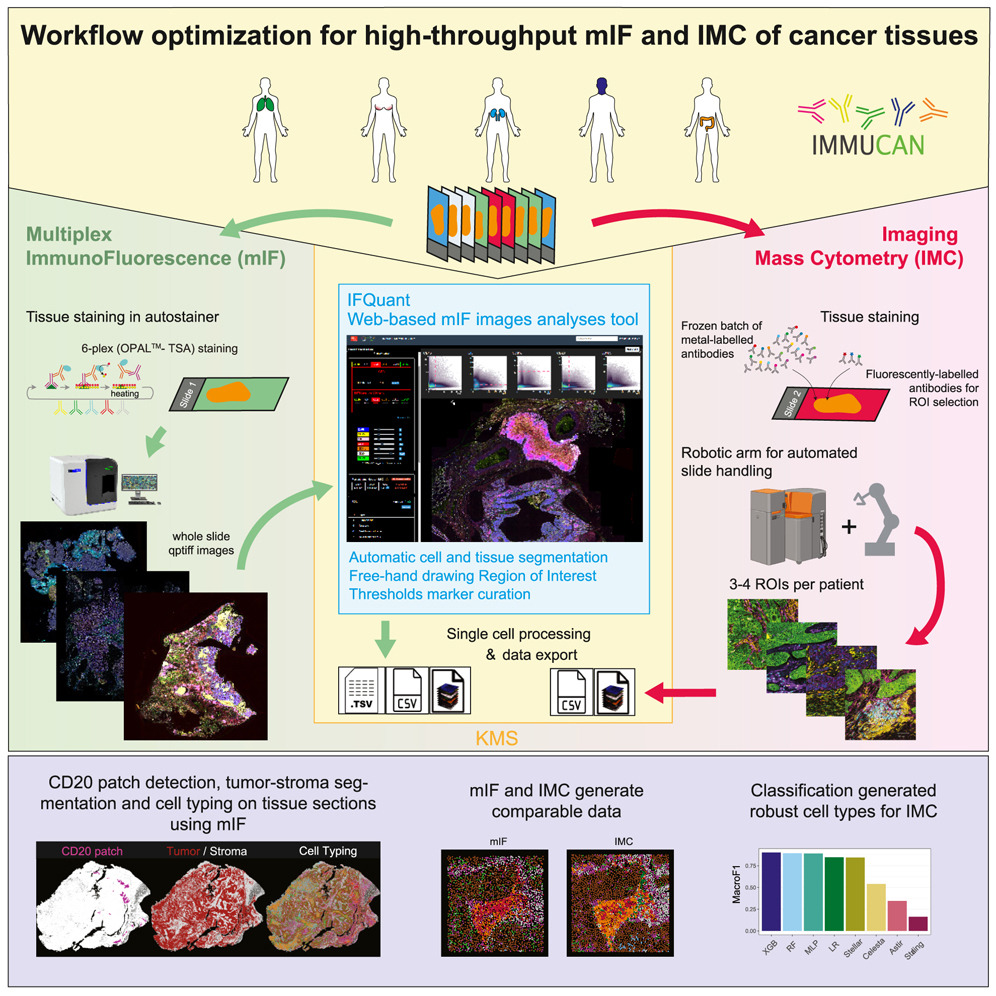
Scalable Imaging Workflows Advance Cancer Tissue Profiling
A new Cell Reports Methods study co-led by the Bodenmiller Lab presents robust, large-scale workflows for imaging mass cytometry and immunofluorescence, enabling immune profiling of thousands of cancer tissues across Europe.
-

CD4 T cells gain innate function after activation
A new study from the Joller Lab reveals that classical T cell activation equips CD4 T cells with an innate-like ability to produce IFN-γ in response to cytokines alone. The findings suggest a broader role for these cells across infections and autoimmunity.
-

Junior Scientist Symposium 2.0: Path to Diverse Career Paths
A full‑day symposium organized entirely by DQBM JUSCOR empowered early‑career researchers with workshops, talks from industry professionals, and networking opportunities to explore academic and non‑academic careers.
-
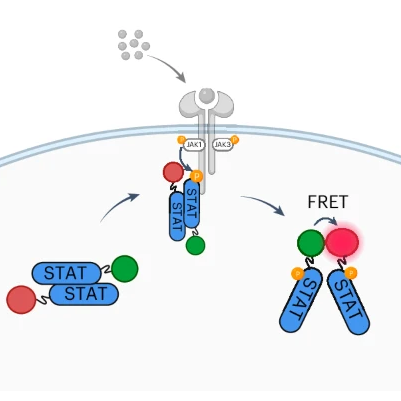
Boyman Lab unveils real-time STAT biosensors
A new study in Nature Chemical Biology introduces STATeLights, biosensors developed by the Boyman Lab to monitor STAT activation in living cells.
-
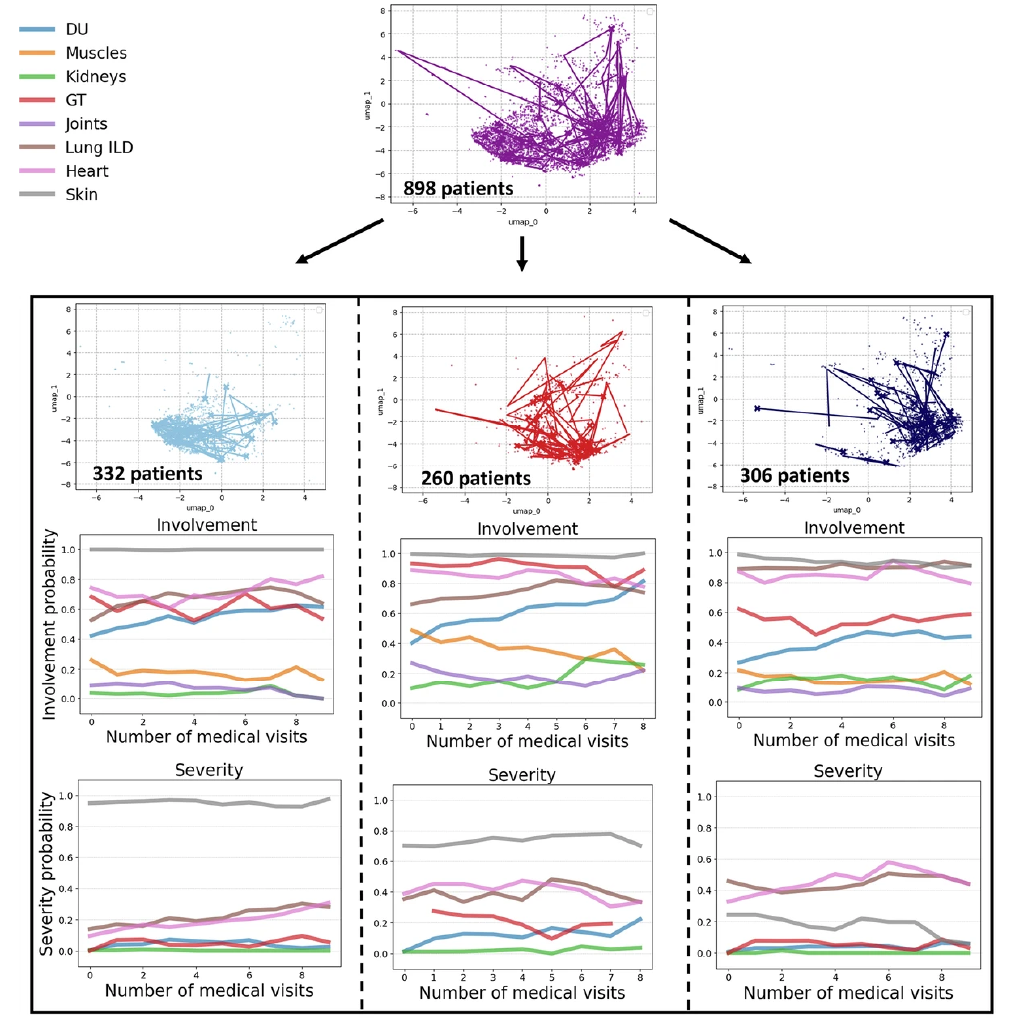
Krauthammer Lab maps SSc disease subtypes
A semi-supervised deep model trained on EUSTAR registry trajectories reveals five hierarchical systemic sclerosis subtypes across eight organs.
-
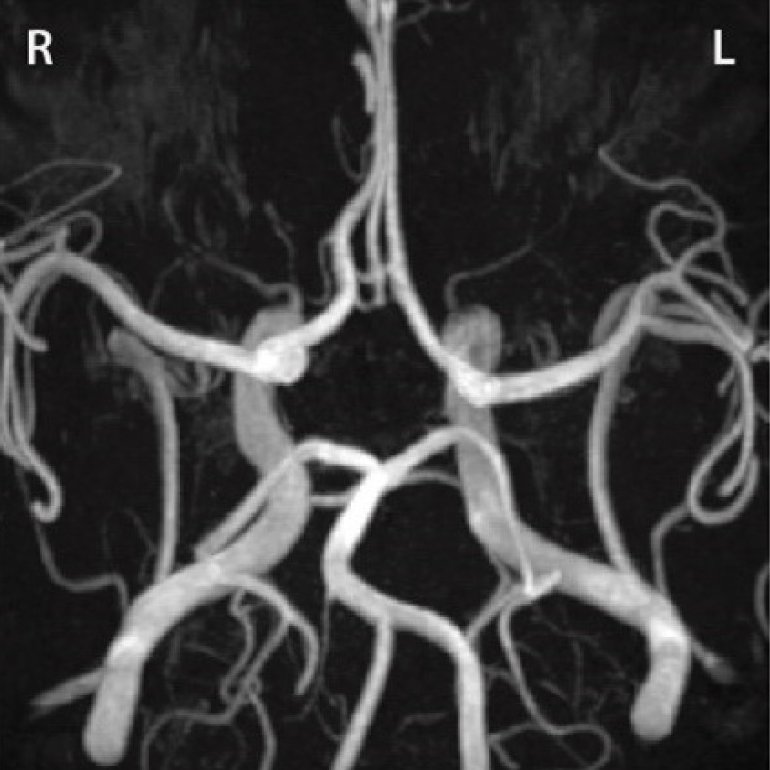
DQBM contributes to CROWN challenge study
A new publication in Medical Image Analysis presents results from the CROWN challenge, benchmarking automated techniques for Circle of Willis artery classification and quantification. The study involved contributions from the Menze Lab at DQBM.
-
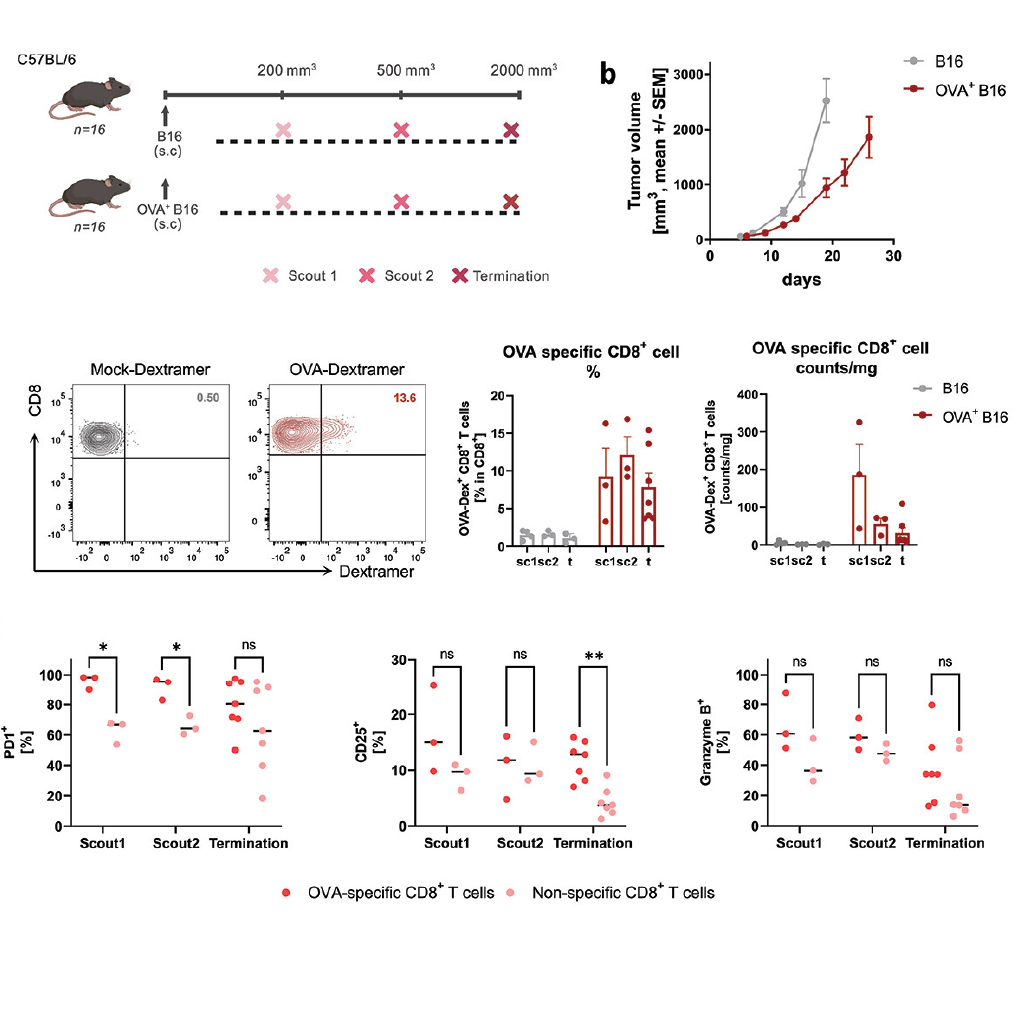
Chronic Antigen Exposure Limits TCB Efficacy in Melanoma
The Joller Lab contributes to a study that reveals that persistent tumor antigen stimulation drives T cell exhaustion, compromising the therapeutic impact of T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs) in melanoma.
-
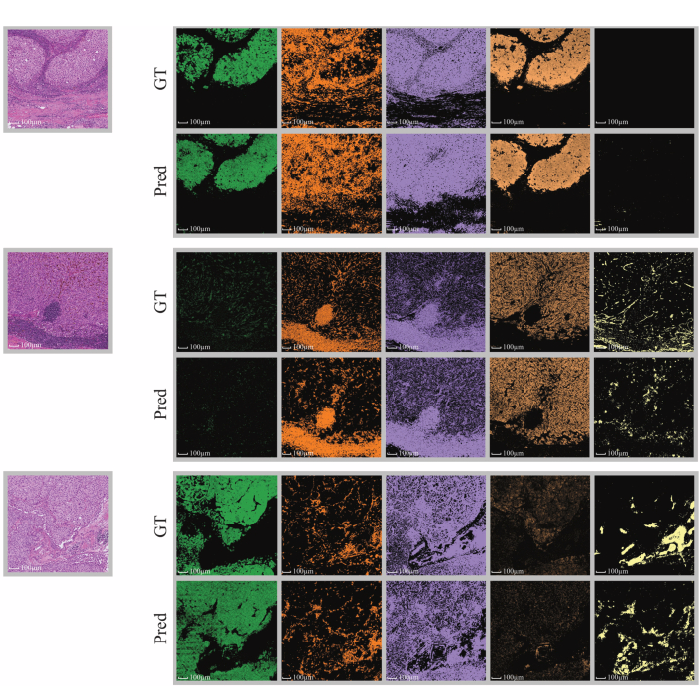
HistoPlexer predicts protein maps from H&E images
A Nature Machine Intelligence study introduces HistoPlexer, a deep learning model that generates whole slide, spatially resolved multiplex protein maps directly from routine H&E histopathology. The approach preserves key spatial biology and improves immune subtype classification and survival prediction.
-
PRIDICT2.0 and ePRIDICT advance prime editing
A new protocol in Nature Protocols introduces PRIDICT2.0 and ePRIDICT, computational tools that streamline pegRNA design for efficient prime editing.
-

ViTa: A Multi-Modal Foundation Model for Cardiac MRI
Suprosanna Shit of the DQBM contributed to a large-scale study presenting ViTa, a foundation model integrating cardiac MRI with patient data for comprehensive heart assessment.
-
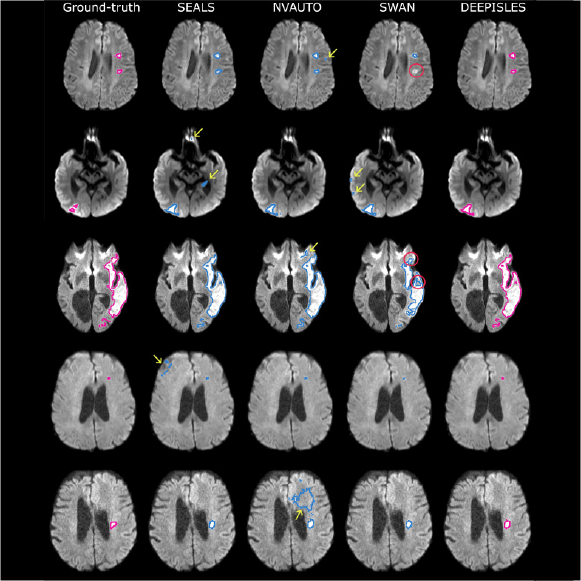
DeepISLES sets new benchmark for stroke MRI segmentation
A DQBM-supported study introduces DeepISLES, a clinically validated AI tool for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation, developed from the ISLES’22 challenge. The algorithm outperforms existing methods in accuracy, generalization, and clinical relevance.
-

Consensus Statement on Digital Twins in Medicine
A DQBM-led study outlines expert recommendations for the responsible use of digital twins in medicine, highlighting strong public interest alongside concerns over autonomy, privacy, and governance.
-

Jaime Grutzendler on imaging neurodegeneration
Visiting Professor Jaime Grutzendler from Yale University delivered a seminar at DQBM on cellular mechanisms of neurodegeneration, hosted in collaboration with the Krauthammer Lab.
-

How S. aureus Survives Calprotectin
New research from the Kümmerli Lab reveals how Staphylococcus aureus withstands the host immune protein calprotectin through combined phenotypic and genetic strategies.
-
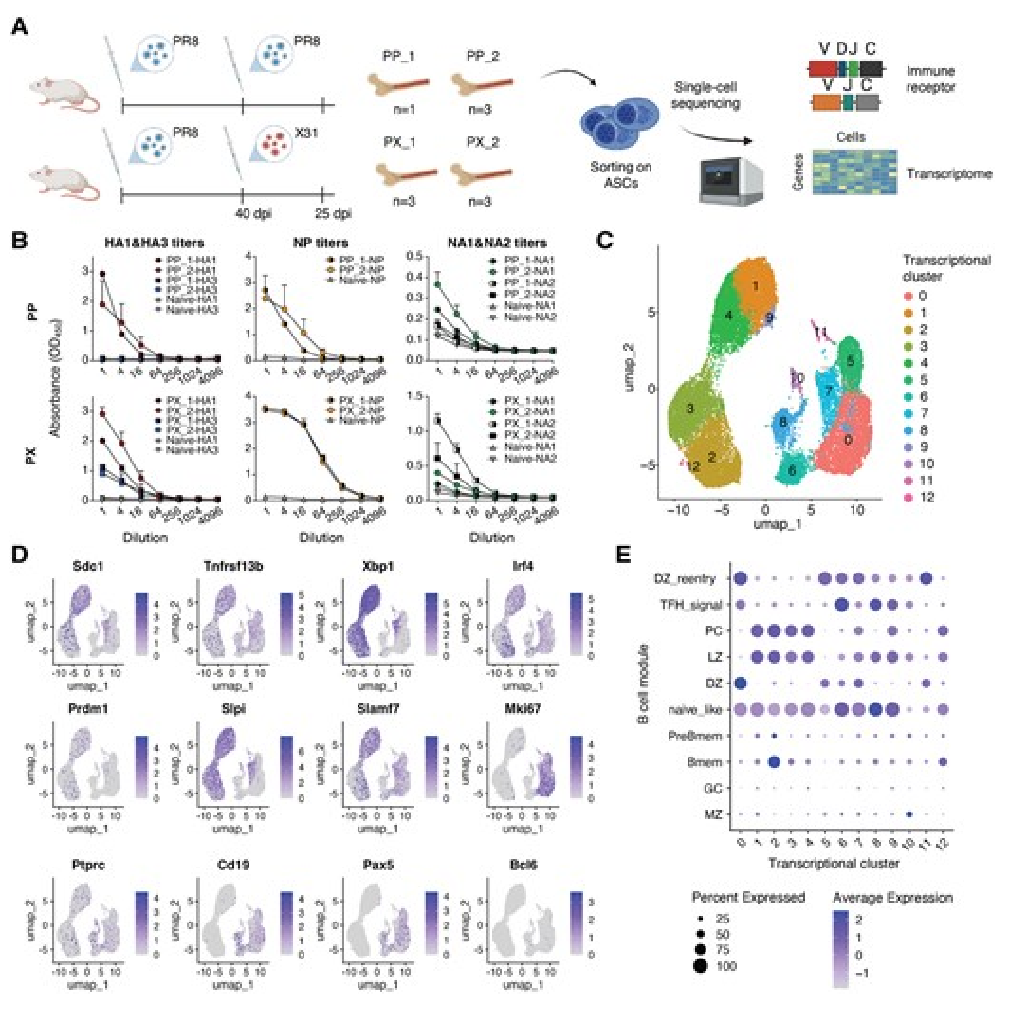
IgG, not IgA, ASCs preferentially target influenza NP
An international team of researchers found that clonally expanded IgG, but not IgA, antibody-secreting cells in bone marrow preferentially target influenza nucleoprotein after infection.
-
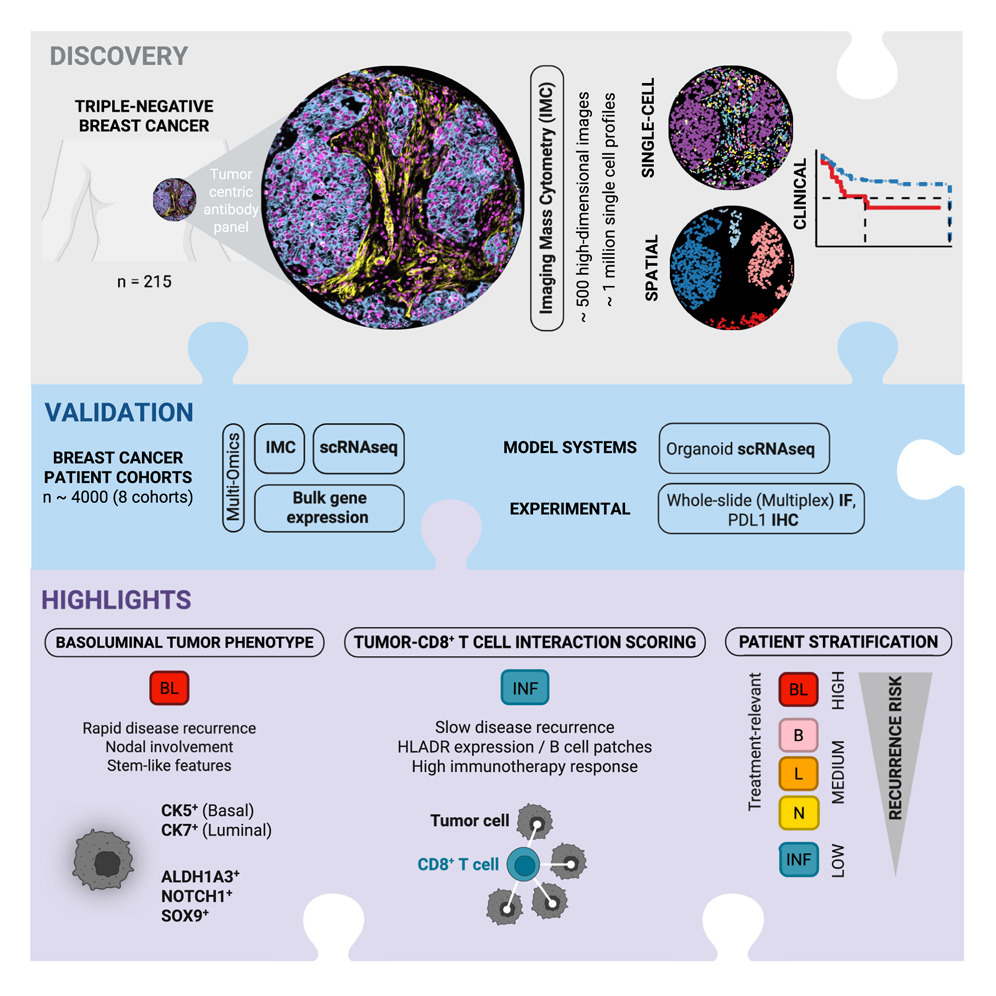
New TNBC Stratification Highlights Prognostic Tumor Cells
Researchers from the Bodenmiller Lab have developed a five-group stratification system for triple-negative breast cancer based on basoluminal tumor cells and immune cell spatial patterns.
-
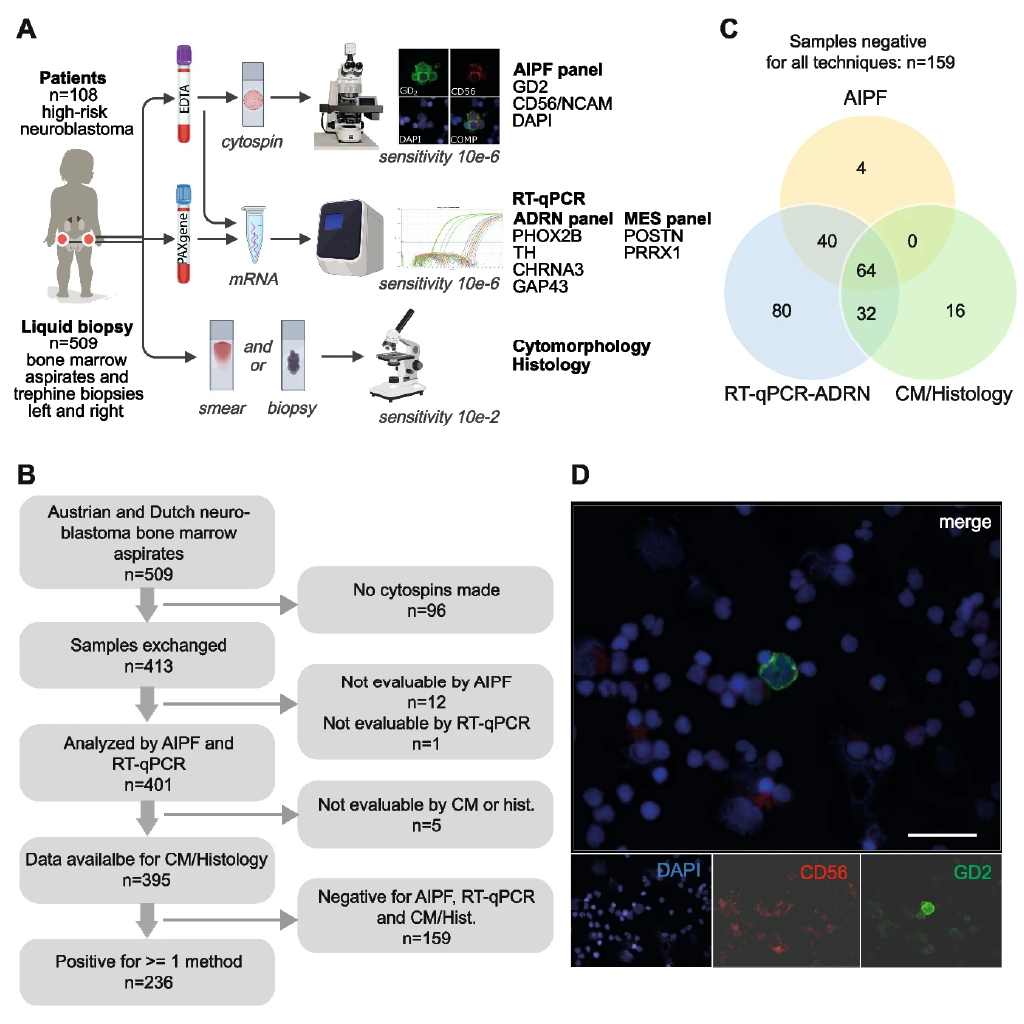
Multi-modal MRD detection boosts neuroblastoma monitoring
A new multi-center study featuring the Bodenmiller Lab demonstrates that combining advanced molecular and imaging techniques greatly improves detection of minimal residual disease in high-risk neuroblastoma, enabling earlier relapse monitoring and better assessment of immunotherapy targets.
-

Magdalini Polymenidou elected EMBO Member
DQBM Professor Magdalini Polymenidou has been elected to the prestigious EMBO Membership, recognizing her outstanding contributions to life sciences research.
-
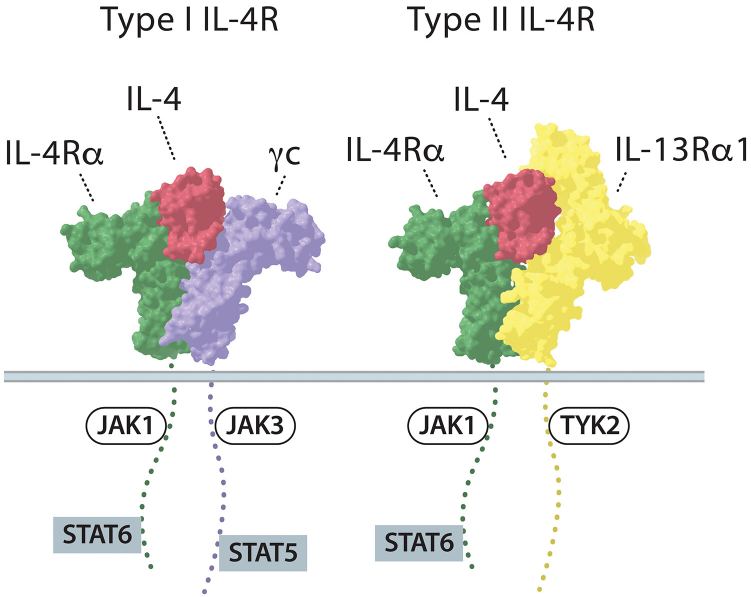
Engineered IL-4 Variants Enable Precise Immune Regulation
Boyman lab researchers introduce chemically synthesized IL-4 variants that provide targeted, receptor-specific immune modulation, with potential for precise treatment of autoimmune diseases.
-
Imaging Reveals Tumor Complexity in Detail
The Bodenmiller Lab applies high-dimensional imaging to guide treatment strategies in melanoma patients.
-

DQBM Retreat Fosters Connection and Innovation
The 2025 DQBM Retreat brought together all groups for three days of science, reflection, and team building in Feldkirch.
-
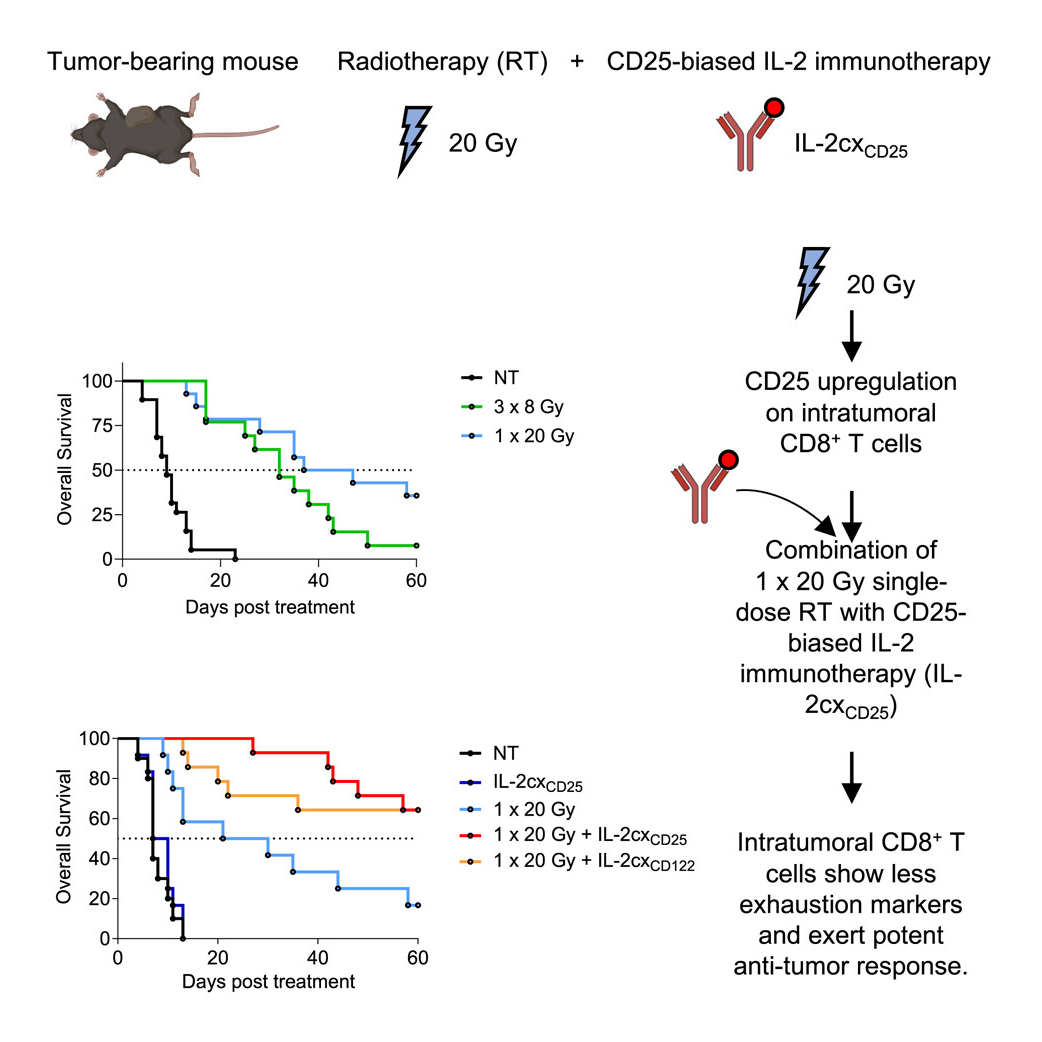
IL-2 Immunotherapy Enhances Radiotherapy in Colon Cancer
Researchers from the Boyman lab reveal that IL-2 immunotherapy reverses T cell exhaustion caused by radiotherapy, boosting anti-cancer immunity in colon cancer models.
-
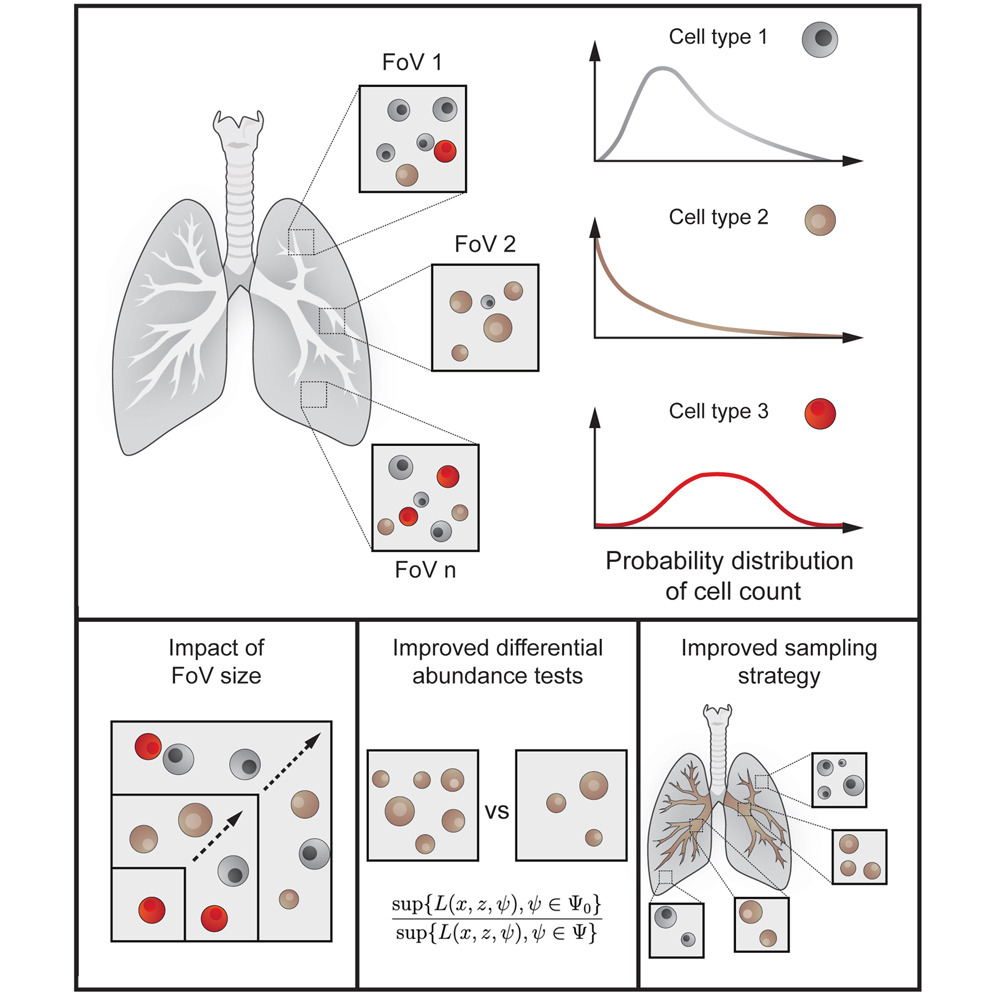
New Statistical Models Improve Multiplexed Imaging Analysis
Bodenmiller lab introduces robust statistical models to enhance the analysis of multiplexed imaging data, boosting sensitivity in clinical tissue studies.
-
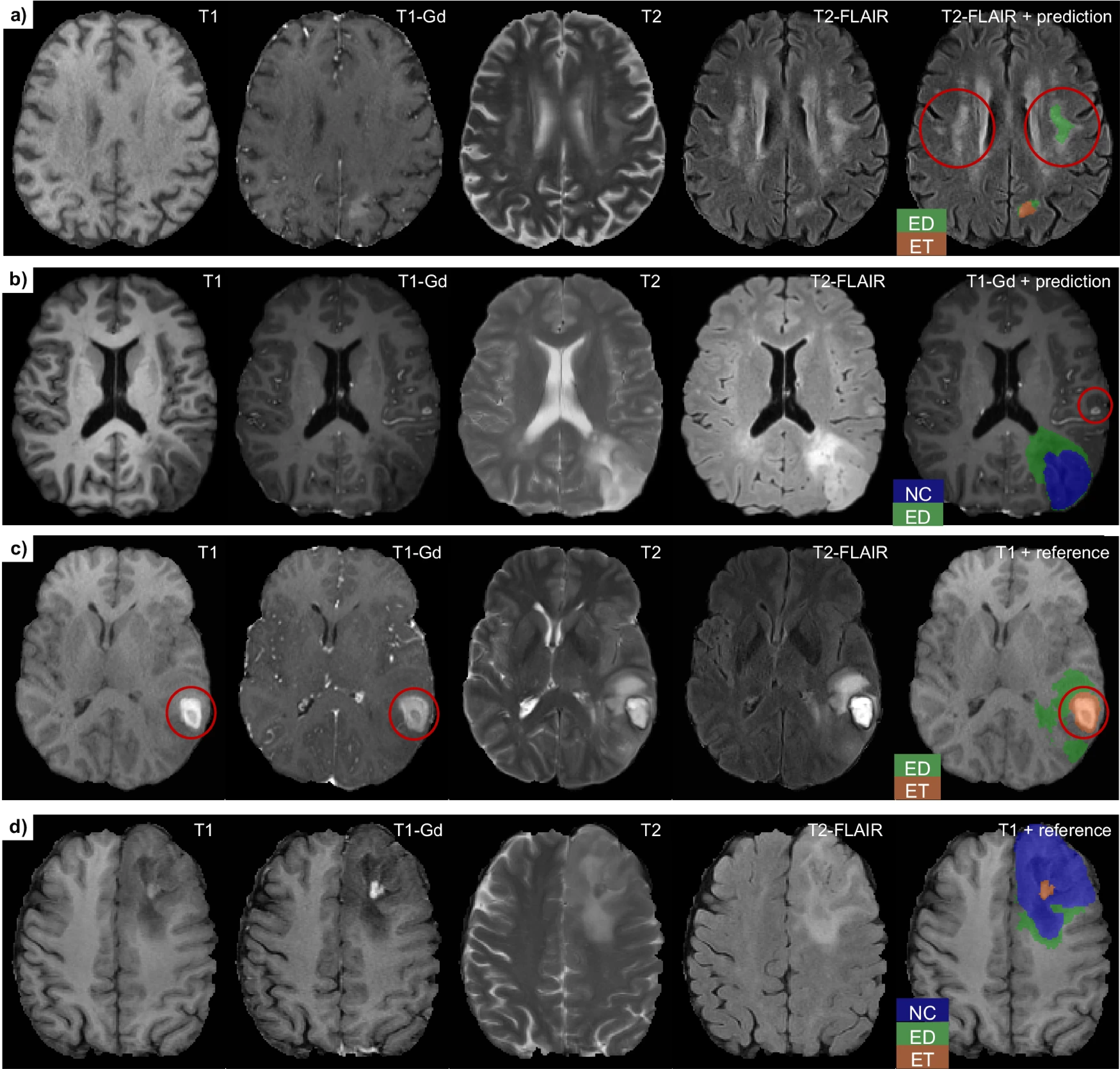
Federated AI Boosts Tumor Segmentation
FeTS Challenge benchmarks federated learning methods for secure brain tumor analysis.
-
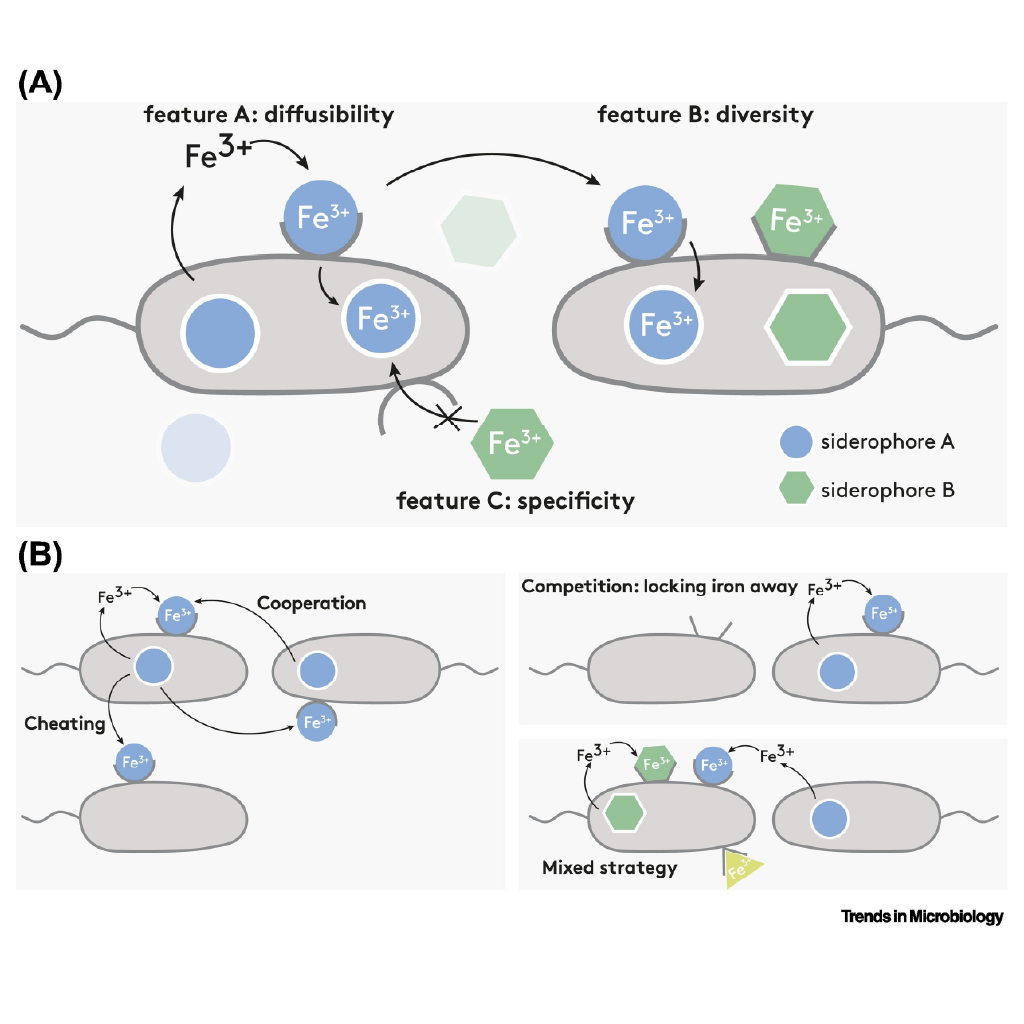
Siderophores as One Health Allies
A new opinion piece in Trends in Microbiology by Rolf Kümmerli and colleagues highlights microbial siderophores as powerful tools to improve environmental, animal, and human health.
-
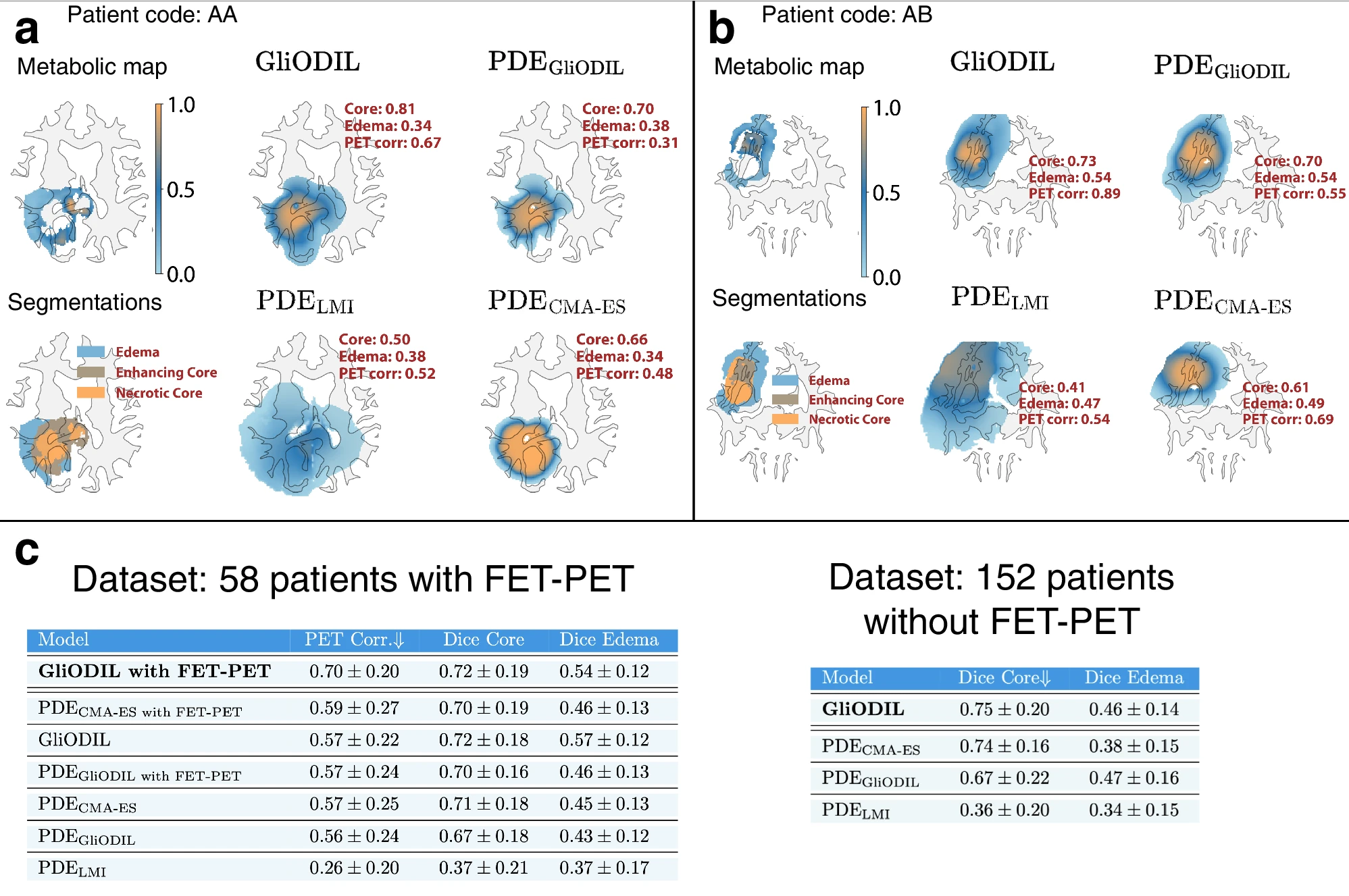
Framework Personalizes Glioma Radiotherapy
FeTS Challenge benchmarks federated learning methods for secure brain tumor analysis.
-
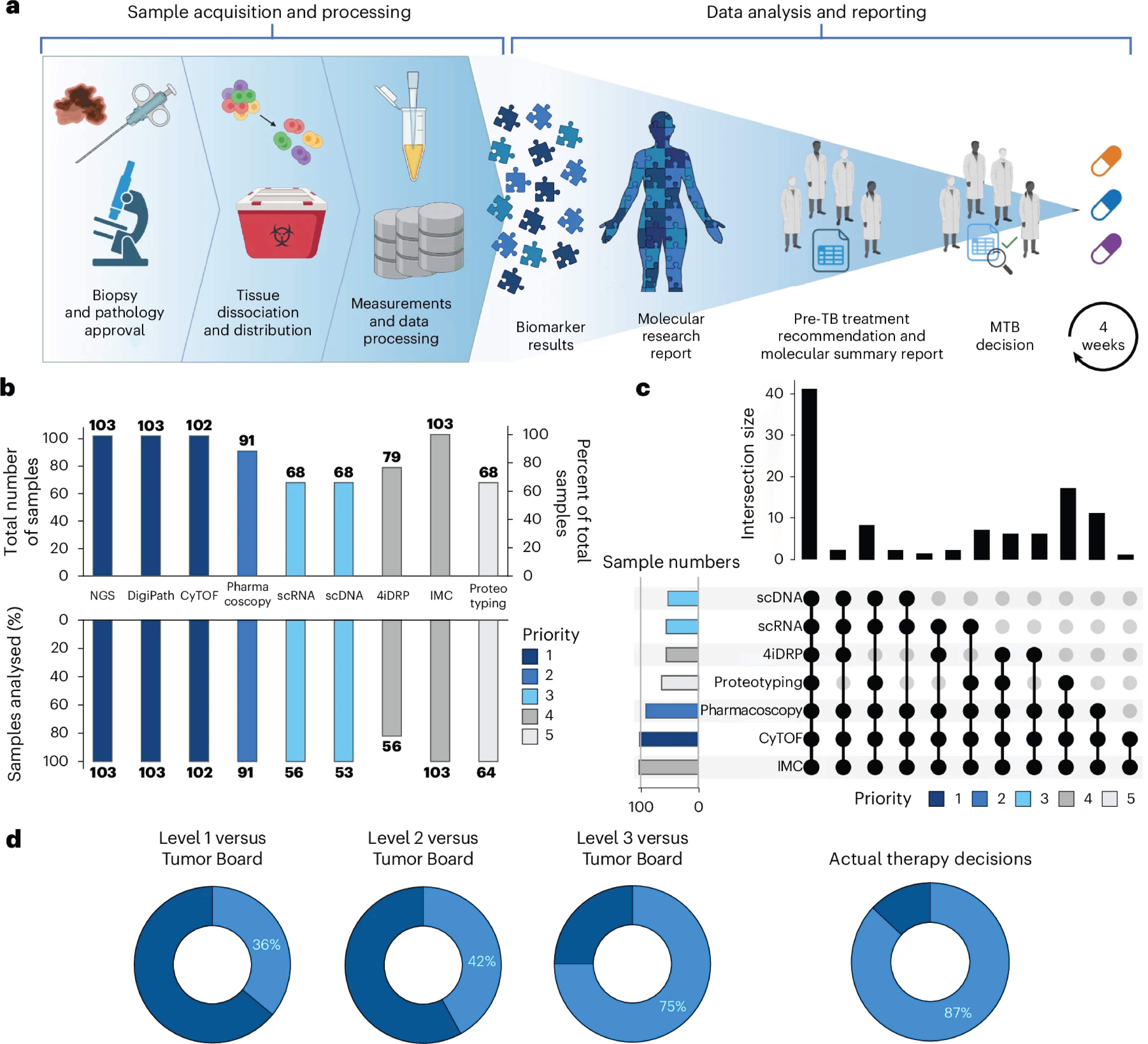
Tumor Profiler Study Confirms Value of Multiomics in Melanoma Care
An international study, with contributions from the Bodenmiller Lab at DQBM, used single-cell multi-omics to characterise immune cell diversity in multiple sclerosis lesions.
-
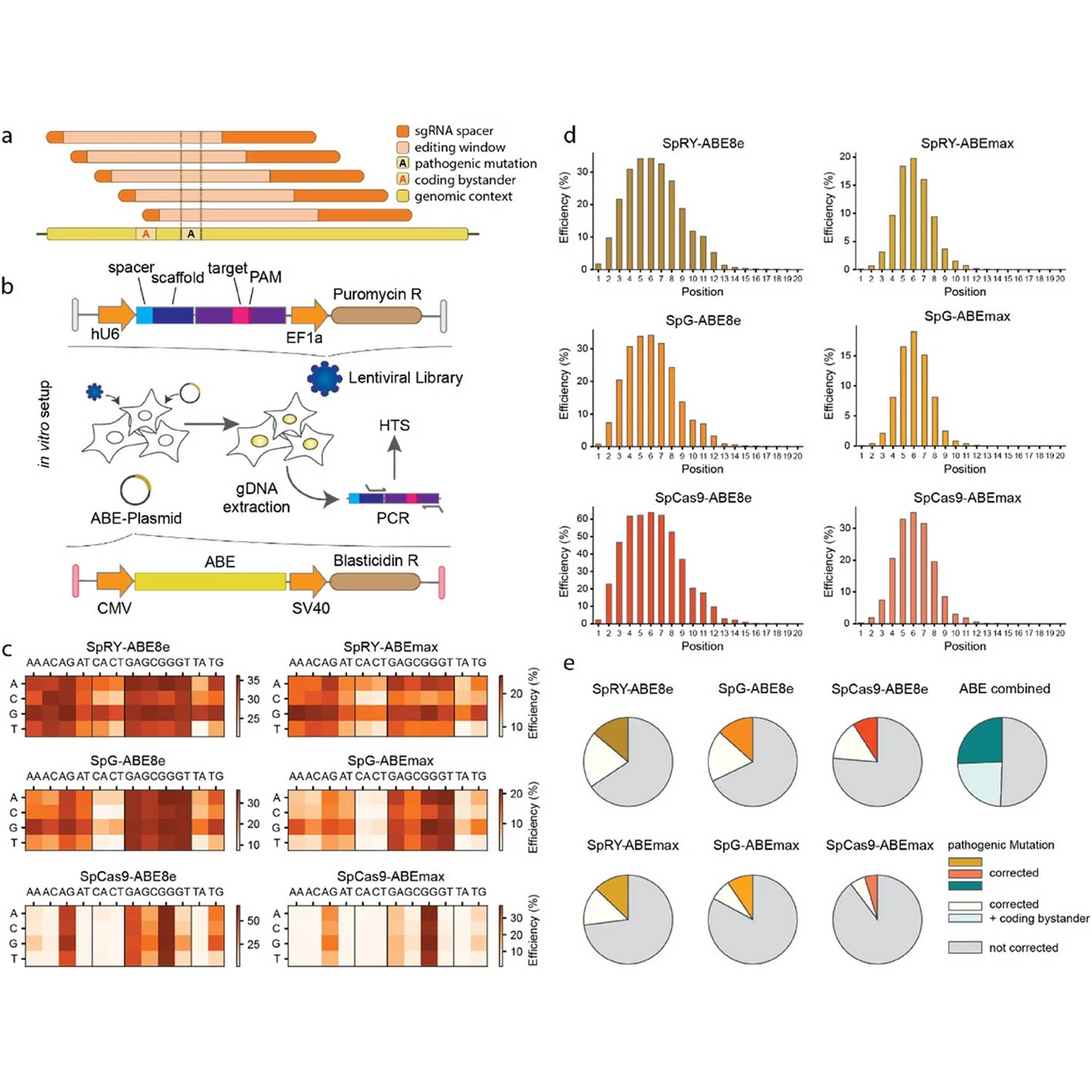
Predicting Gene Editing Outcomes with Deep Learning
The Krauthammer Lab contributes to a major advance in predicting adenine base editing outcomes using BEDICT2.0, a machine learning model validated in both in vitro and in vivo settings.
-
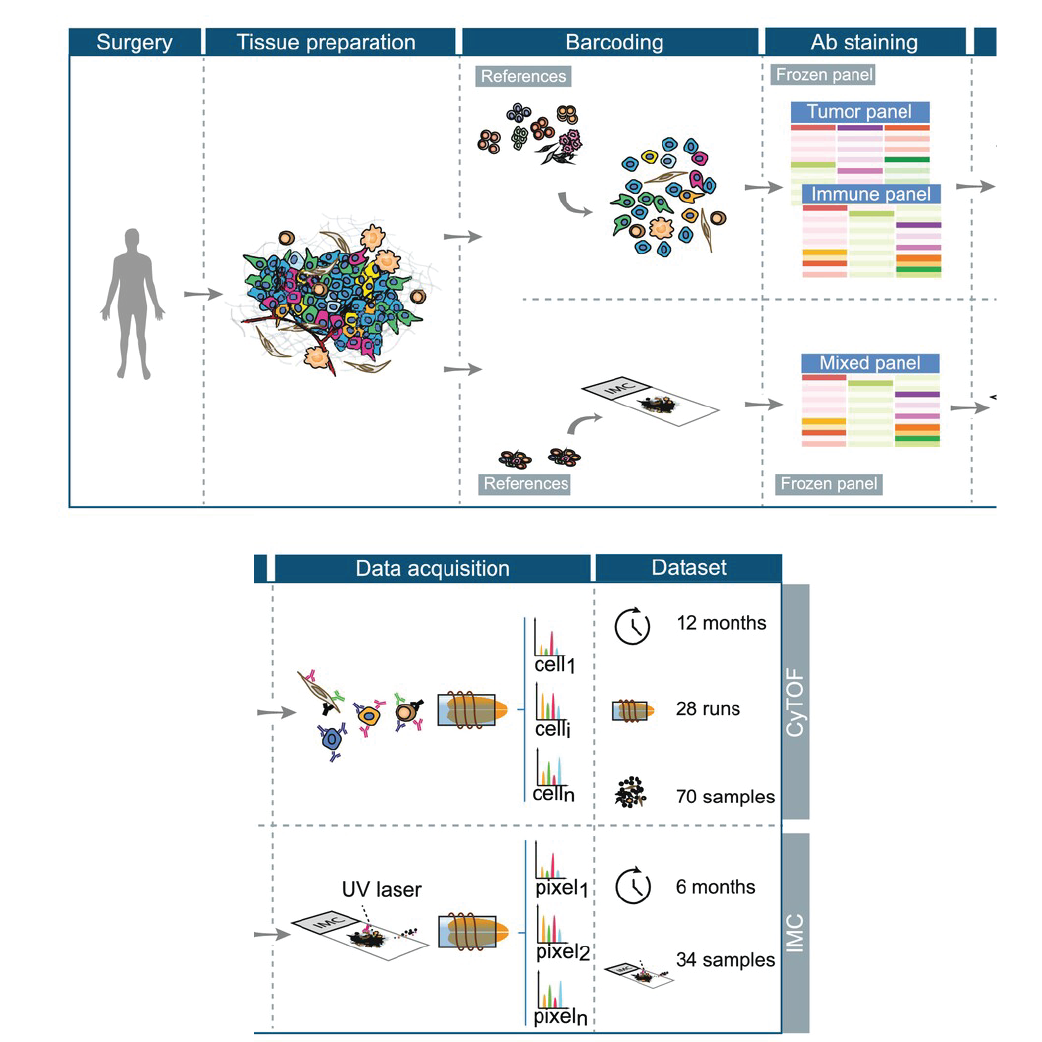
Standardized Mass Cytometry Advances Clinical Decision-Making
Researchers from the Bodenmiller lab help establish standardized protocols for mass cytometry, advancing its reliability for clinical oncology applications.
-
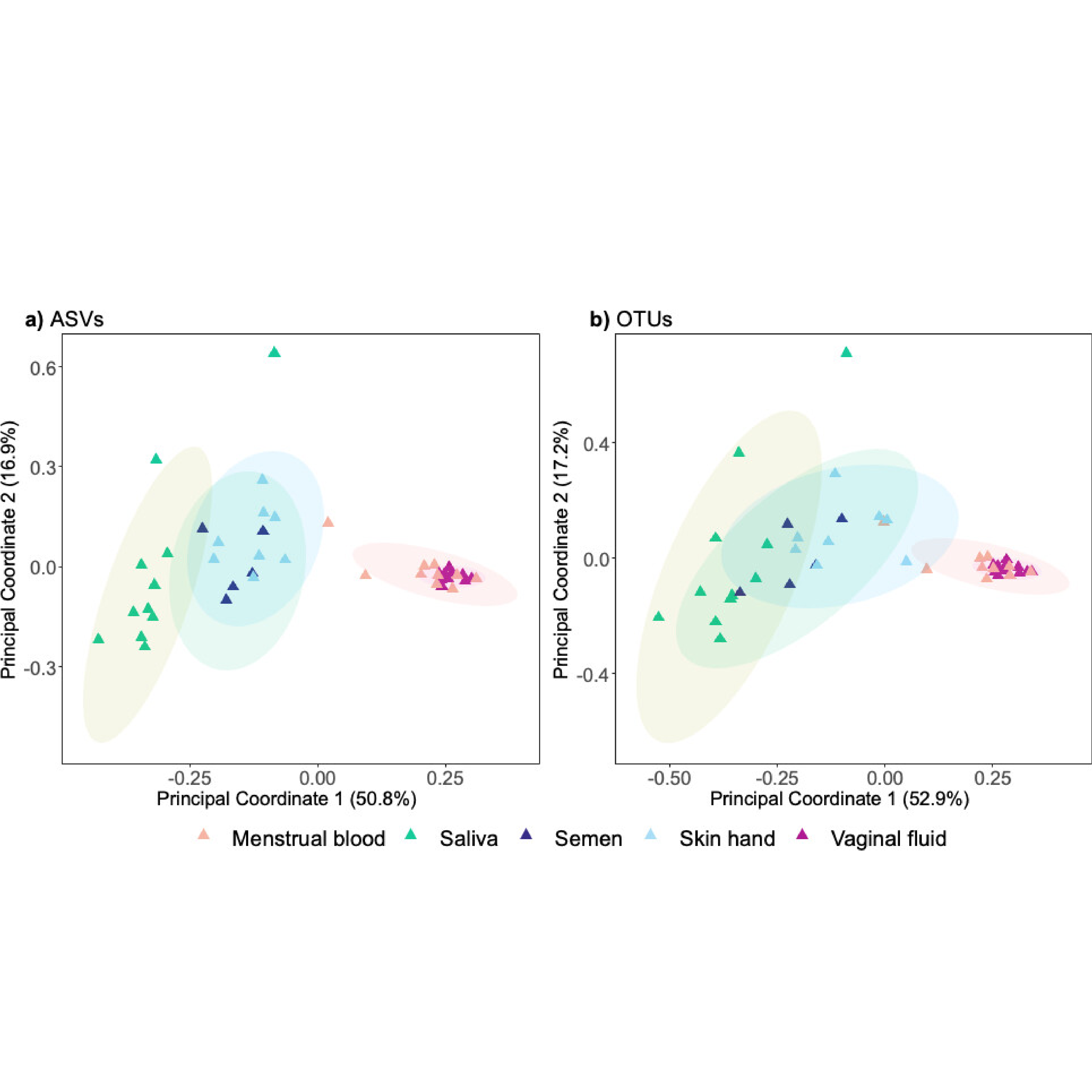
New Microbiome Pipeline Improves Forensic Body Fluid Identification
A collaborative study involving the Kümmerli lab establishes standardized microbiome-based methods for forensic body fluid identification, significantly enhancing the accuracy of crime scene analysis.
-

JUSCOR Easter Event
This Easter, the JUSCOR team brought the DQBM community together for an afternoon of games, laughter, and an egg-citing hunt at the Green Lab Kitchen.
-

Seeded TDP-43 Aggregation Model Developed at DQBM Reveals Early Neurodegenerative Signatures
A groundbreaking study from the Polymenidou lab at DQBM, published in Neuron, introduces a new cellular model that links TDP-43 aggregation to loss of function—key features in ALS and FTD.
-
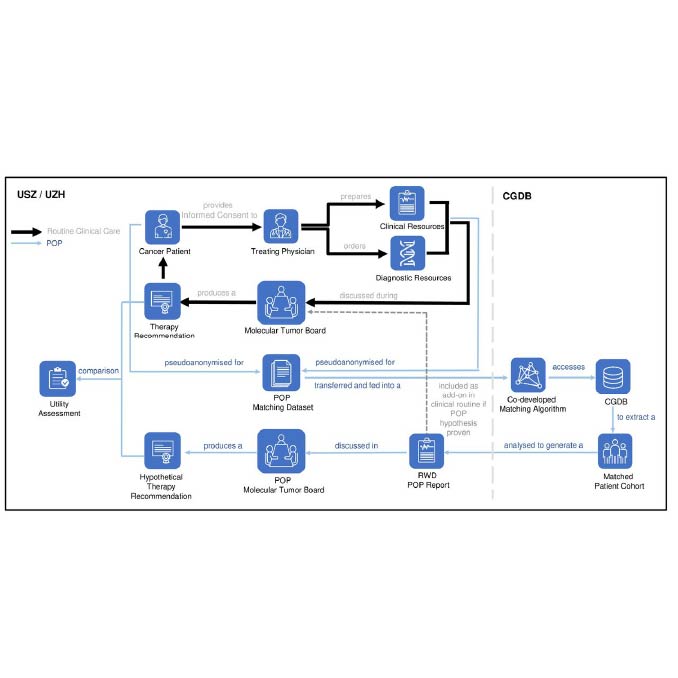
Precision Oncology Program Launches Study Protocol
DQBM and partners introduce POP, a study integrating real-world data and imaging mass cytometry to enhance decision-making in cancer treatment.
-
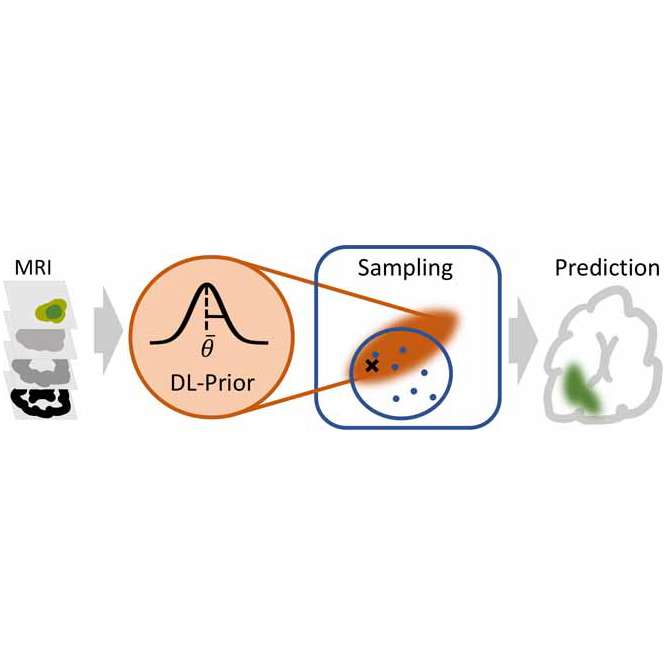
Deep Learning Prior Speeds Up Tumor Modeling
A hybrid framework accelerates glioblastoma modeling, supporting precise radiotherapy planning.
-
DQBM Kicks Off Spring with First Mini-Symposium of 2025
On March 6, DQBM held its first mini-symposium of the spring term at Irchel Campus, bringing together all groups for scientific exchange, collaboration, and community building.
-
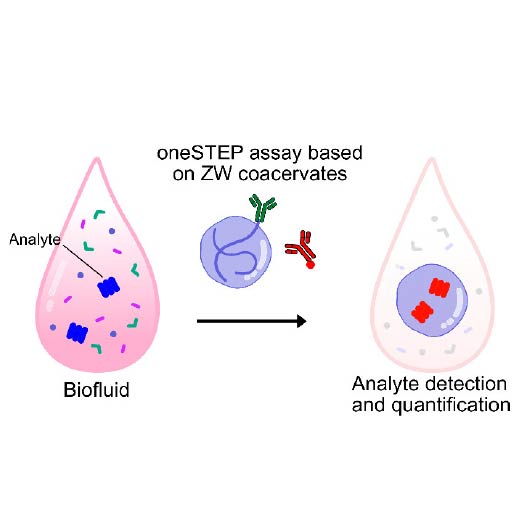
One-Step Assay Enables Rapid Biomarker Detection
The Boyman Lab co-develops a single-step immunoassay using phase-separated polymers, offering wash-free biomarker quantification in complex fluids.
-
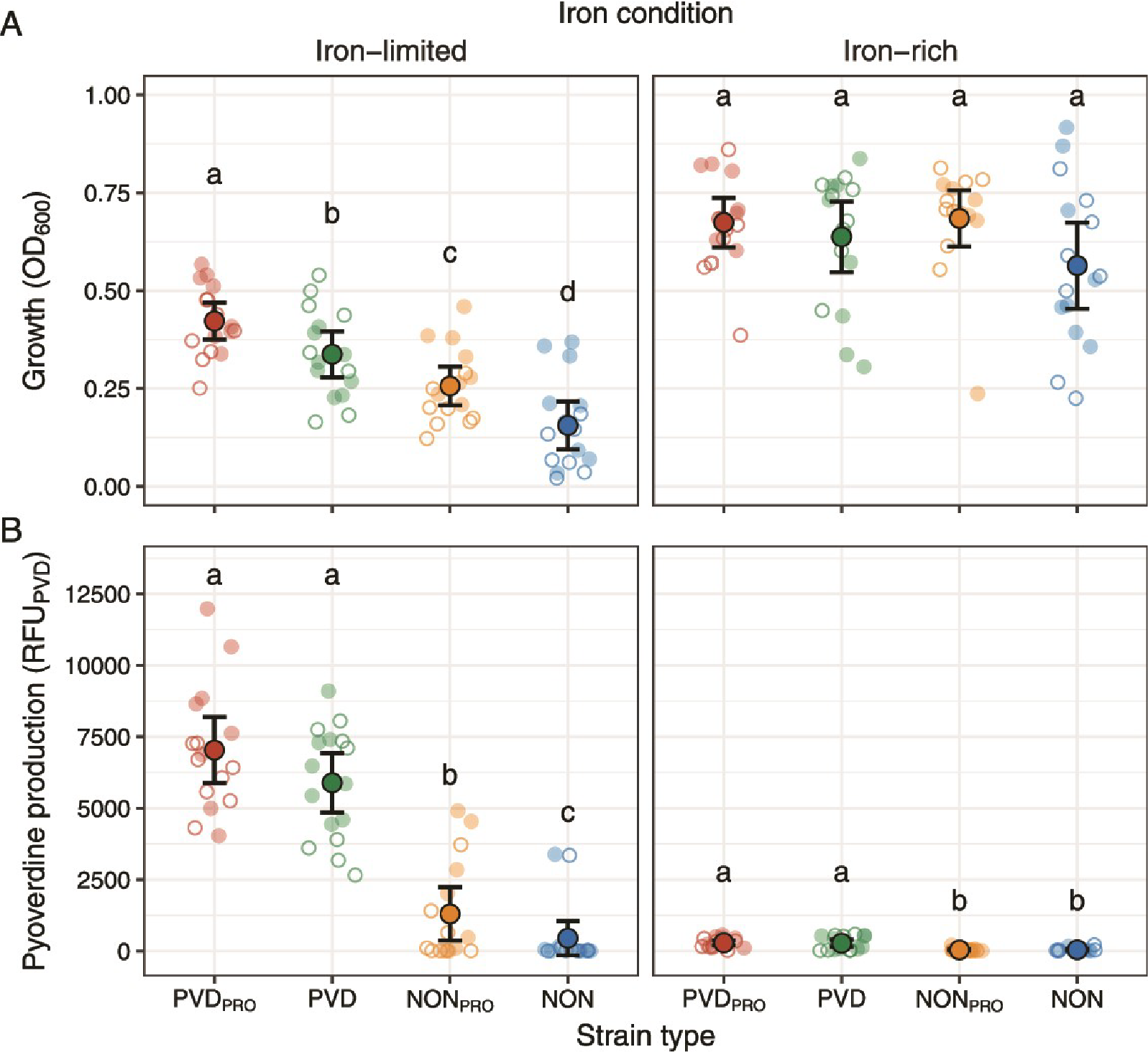
Strain Identity Crucial for Bacterial Community Functioning
A study co-authored by the Kümmerli lab finds that individual strain identities play a greater role than interactions in shaping the functioning of bacterial communities, with implications for microbiome engineering.
-

Prof. Onur Boyman Joins DQBM, Enhancing Clinical and Translational Immunology Research
Prof. Dr. Onur Boyman joined the DQBM on February 1, 2025, bringing his expertise in immunology and cytokine-based therapies. His appointment strengthens DQBM’s clinical and translational research and reinforces its mission to connect basic science with medical application.
-
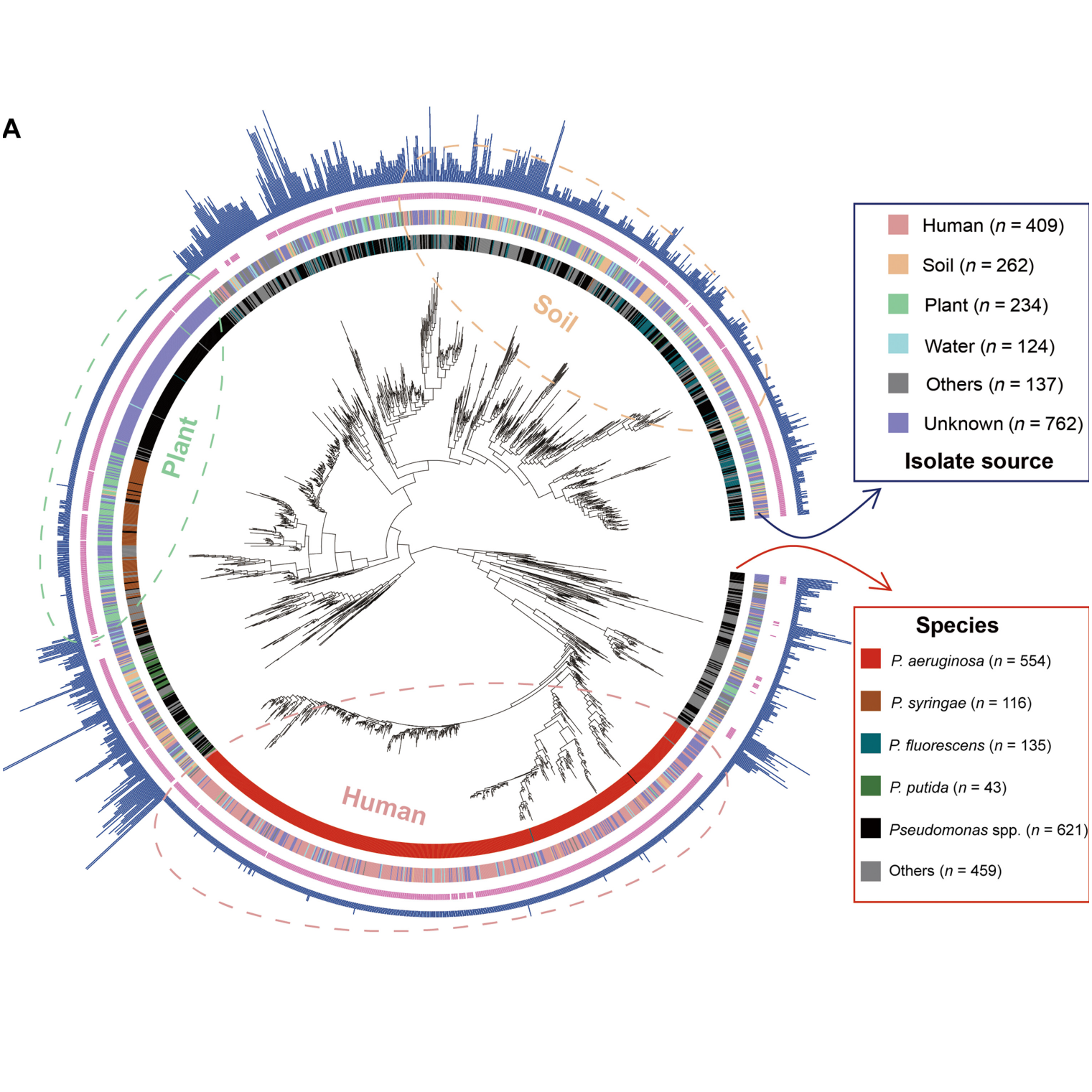
Coevolution Algorithm Reveals Bacterial Iron Interaction Networks
A collaborative study involving the Kümmerli lab introduces a powerful computational approach that reveals how bacterial iron-scavenging genes coevolve, providing insights into pathogen-specific interaction networks.
-
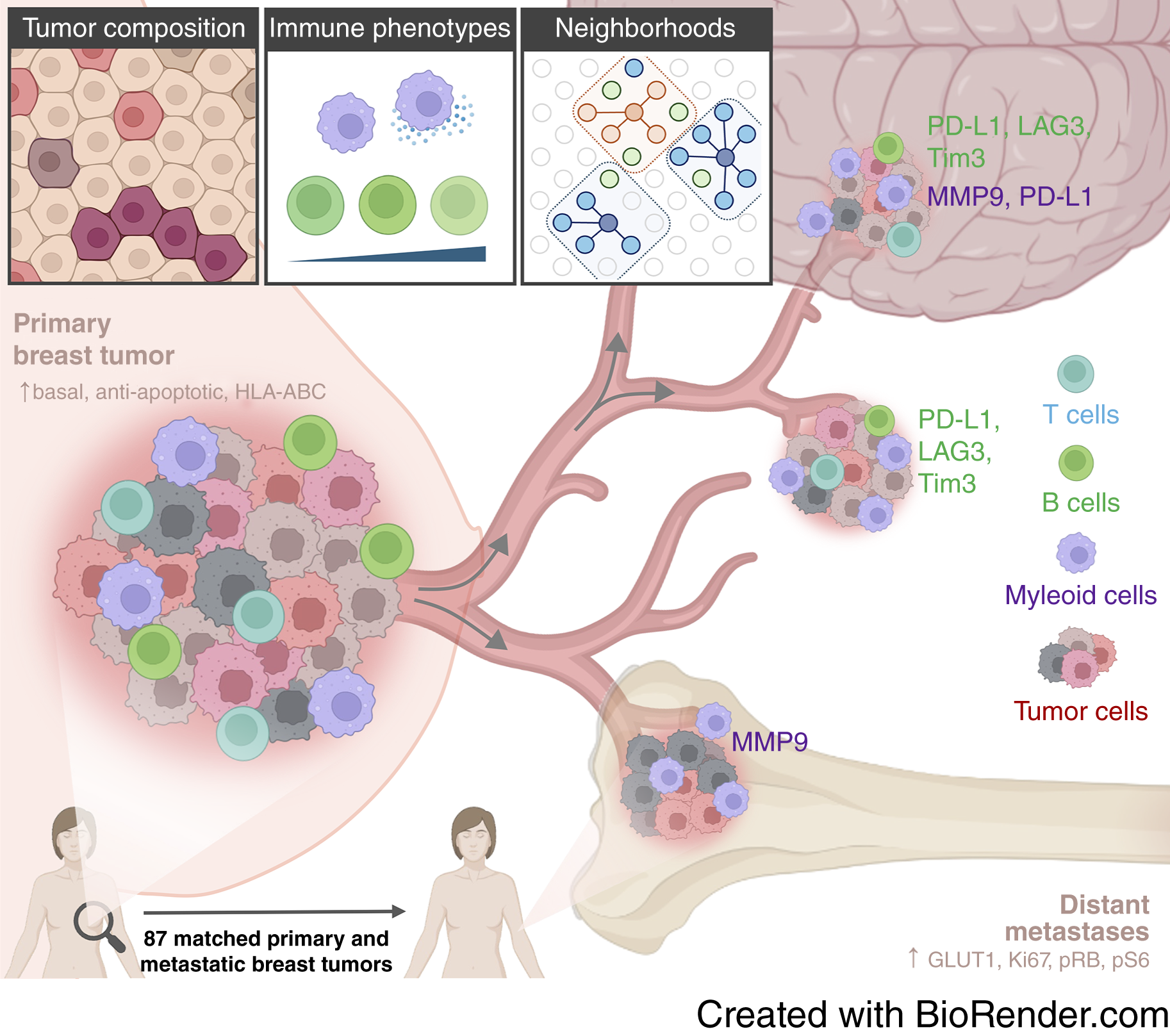
Breast Cancer Metastases Retain Tumor Cell Types but Shift Immune Profiles
New single-cell imaging research from the Bodenmiller Lab reveals that while breast cancer metastases retain the cancer cell types of primary tumors, their immune cell environments undergo distinct changes.
DQBM News Archive
For older news, check out the DQBM News Archive.