IL-2 Immunotherapy Enhances Radiotherapy in Colon Cancer
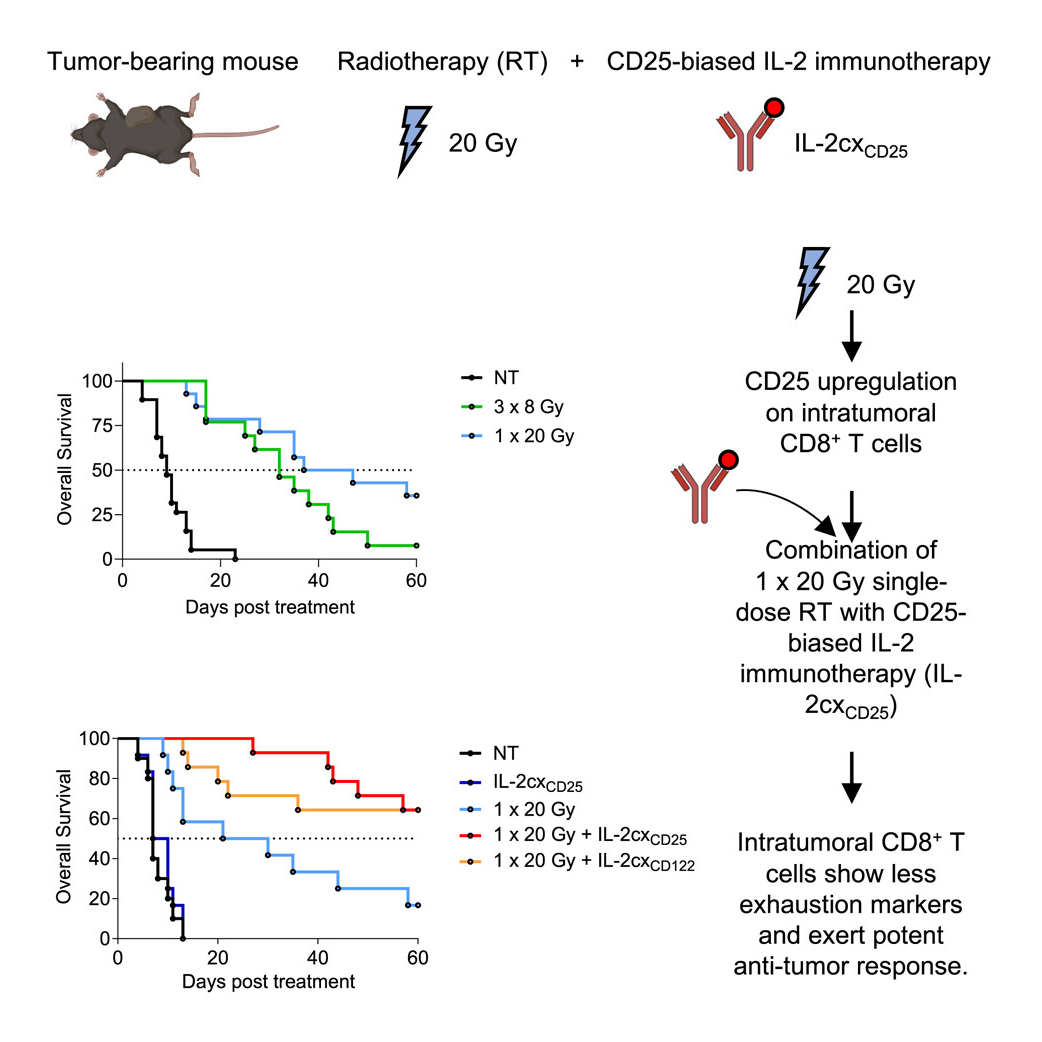
A recent study published in iScience by researchers from the DQBM Boyman Lab and colleagues demonstrates that IL-2 immunotherapy can effectively counteract T cell exhaustion following radiotherapy, enhancing tumor control in mouse colon cancer models.
Radiotherapy is essential for treating many cancers but can lead to T cell exhaustion, limiting immune effectiveness. In this study, the team found that high-dose radiotherapy (RT) temporarily increases CD25 expression on tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Leveraging this finding, they tested IL-2 immunotherapy specifically targeting CD25 or CD122 receptors. Both IL-2 therapies, when timed after RT, greatly improved immune responses, reducing exhaustion markers on CD8+ T cells and controlling tumor growth.
Notably, this combined treatment was effective against both irradiated and non-irradiated distant tumors—a phenomenon known as the "abscopal effect." The results highlight IL-2 therapy as a promising addition to radiotherapy, potentially providing sustained and systemic anti-tumor immunity.
Publication Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2025.112639