Multi-modal MRD detection boosts neuroblastoma monitoring
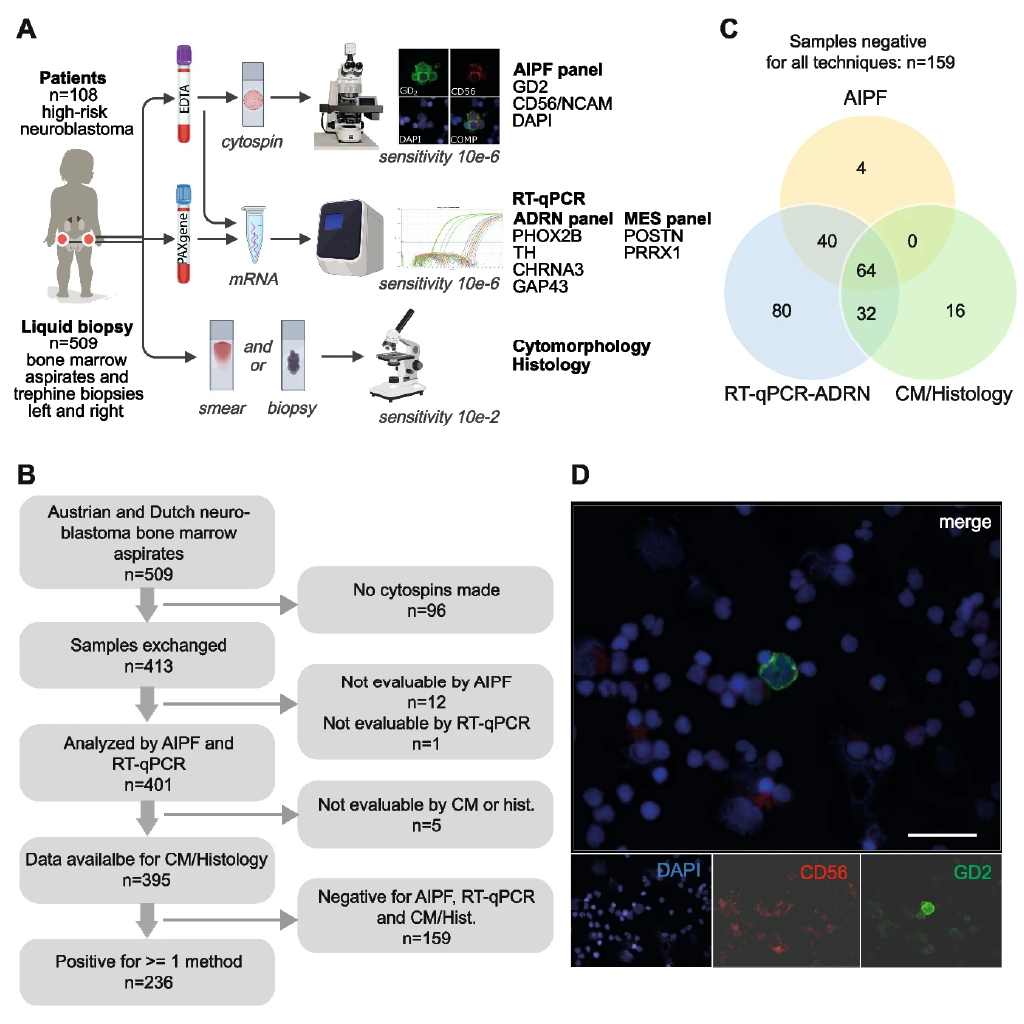
Researchers, including the DQBM Bodenmiller Lab, have shown that integrating high-sensitivity reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) with automated immunofluorescence and interphase FISH (AIPF) significantly outperforms standard bone marrow diagnostics in detecting minimal residual disease (MRD) in high-risk neuroblastoma. In 509 samples from 108 patients, the combined approach identified many cases missed by conventional cytomorphology and histology. Beyond MRD detection, the methods tracked tumor cell state shifts between adrenergic and mesenchymal phenotypes and quantified immunotherapy targets such as GD2 and CD56, revealing potential therapy resistance mechanisms. This work paves the way for standardized, sensitive MRD assessment in international clinical trials, with the potential to guide timely, personalized interventions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-025-03481-w